CAT Exam > CAT Questions > A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique ...
Start Learning for Free
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?
Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the ...
Understanding the Pricing Strategy
The fruit seller's pricing strategy is as follows:
- If the number of oranges bought is less than or equal to 100, the price per orange is fixed at Rs.10.
- For every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is applied to the entire bunch.
Calculating Revenue for Different Values of 'n'
To find the value of 'n' that maximizes revenue, we need to calculate the revenue for different values of 'n' and identify the maximum revenue.
Let's calculate the revenue for 'n' oranges using the given pricing strategy:
If 'n' is less than or equal to 100:
- The price per orange is Rs.10.
- Therefore, the revenue for 'n' oranges is 10 * n.
If 'n' is greater than 100:
- The price per orange is Rs.10 minus the discount of (1/40) per orange.
- The total discount for the additional oranges is (n - 100) * (1/40).
- Therefore, the price per orange for the additional oranges is Rs.10 - (1/40).
- The revenue for 'n' oranges is (10 * 100) + [(n - 100) * (10 - (1/40))].
Finding the Maximum Revenue
To find the value of 'n' that maximizes revenue, we need to compare the revenue for different values of 'n' and identify the maximum revenue.
Let's calculate the revenue for different values of 'n' and find the maximum:
For n = 100:
- Revenue = 10 * 100 = Rs.1000.
For n = 101:
- Revenue = (10 * 100) + [(101 - 100) * (10 - (1/40))] = 1000 + (1 * 9.975) = Rs.1009.975.
For n = 102:
- Revenue = (10 * 100) + [(102 - 100) * (10 - (1/40))] = 1000 + (2 * 9.95) = Rs.1019.9.
Similarly, we can calculate the revenue for other values of 'n'.
Identifying the Maximum Revenue
By calculating the revenue for different values of 'n', we can observe that the revenue initially increases as 'n' increases. However, after a certain point, the revenue starts decreasing. We need to find the value of 'n' where the revenue is maximum.
Based on the calculations, we can observe that the maximum revenue is obtained when 'n' is 250, which is Rs.2475.
Therefore, the value of 'n' that maximizes revenue is 250.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the ...
Revenue from the sale of 100 oranges = 100 x 10 = 1000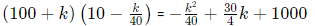
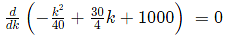
⇒ Let the revenue be maximum for kk additional oranges sold.
Hence the new revenue would be
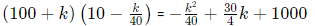
⇒ The value will be maximum at the point where this function is differentiated and then equated to zero.
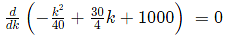
On solving, we get k = 150k = 150
Thus, the value of the function would be maximum at k = 150
Therefore, the value of ‘n’ for which the revenue would be maximum is given by
(100 + 150) = 250
Hence, the required answer is 250.

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|
Similar CAT Doubts
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? for CAT 2025 is part of CAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CAT exam syllabus. Information about A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?.
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? for CAT 2025 is part of CAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CAT exam syllabus. Information about A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for CAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A fruit seller sells oranges using a unique pricing strategy: if the number of oranges you buy is less than or equal to 100, you will have to pay Rs.10 per orange. However, the shopkeeper offers a discount such that for every additional orange above 100, a discount of Rs. (1/40) per orange is levied on the entire bunch. If the seller plans to put a box for sale having ‘n’ oranges, what should be the value of ‘n’ such that the revenue from this box is maximized?Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice CAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























