Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A 120V battery supplies RL load through chop...
Start Learning for Free
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.
Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode...
Understanding the Chopper Operation
In a chopper circuit, the relationship between Ton and Toff (the time the switch is ON and OFF) is crucial for analyzing the load current in RL circuits.
Given Parameters
- Battery Voltage (V) = 120V
- Load Resistance (R) = 5Ω
- Load Inductance (L) = 60mH
- Load Current (I) varies between 7A and 9A
Calculating Average Current (Iavg)
- Average Load Current (Iavg) = (Imin + Imax) / 2
- Iavg = (7A + 9A) / 2 = 8A
Understanding Ton and Toff
- During Ton, the chopper is ON, and the current increases through the inductor.
- During Toff, the chopper is OFF, and the inductor current flows through the freewheeling diode.
Inductor Voltage and Current Relationships
- The inductor's voltage can be expressed as:
V = L * (di/dt)
- The energy stored in the inductor during Ton contributes to the current during Toff.
Applying the Formula for Ton/Toff Ratio
- The average voltage across the inductor during switching can be represented as:
V = Iavg * R
- Calculating the voltage drop:
V = 8A * 5Ω = 40V
- The remaining voltage across the inductor:
VL = V - V = 120V - 40V = 80V
Finding Ton/Toff
- The ratio Ton/Toff can be derived from the energy balance in the inductor.
- Since the current varies linearly, and using the values of R and L, it can be shown that the derived relationship gives a ratio of Ton/Toff = 0.5.
Conclusion
The calculated ratio Ton/Toff = 0.5 indicates that for every 1 unit of time the chopper is ON, it is OFF for 2 units, establishing a balanced operation of the chopper circuit with the RL load.
In a chopper circuit, the relationship between Ton and Toff (the time the switch is ON and OFF) is crucial for analyzing the load current in RL circuits.
Given Parameters
- Battery Voltage (V) = 120V
- Load Resistance (R) = 5Ω
- Load Inductance (L) = 60mH
- Load Current (I) varies between 7A and 9A
Calculating Average Current (Iavg)
- Average Load Current (Iavg) = (Imin + Imax) / 2
- Iavg = (7A + 9A) / 2 = 8A
Understanding Ton and Toff
- During Ton, the chopper is ON, and the current increases through the inductor.
- During Toff, the chopper is OFF, and the inductor current flows through the freewheeling diode.
Inductor Voltage and Current Relationships
- The inductor's voltage can be expressed as:
V = L * (di/dt)
- The energy stored in the inductor during Ton contributes to the current during Toff.
Applying the Formula for Ton/Toff Ratio
- The average voltage across the inductor during switching can be represented as:
V = Iavg * R
- Calculating the voltage drop:
V = 8A * 5Ω = 40V
- The remaining voltage across the inductor:
VL = V - V = 120V - 40V = 80V
Finding Ton/Toff
- The ratio Ton/Toff can be derived from the energy balance in the inductor.
- Since the current varies linearly, and using the values of R and L, it can be shown that the derived relationship gives a ratio of Ton/Toff = 0.5.
Conclusion
The calculated ratio Ton/Toff = 0.5 indicates that for every 1 unit of time the chopper is ON, it is OFF for 2 units, establishing a balanced operation of the chopper circuit with the RL load.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode...
Given: Vs = 120 V, R = 5 Ω, L = 60 mH, I0 = 7A to 9A
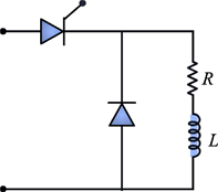
Average output current,
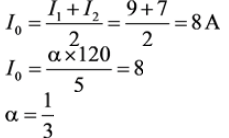
Applying KVL during TON,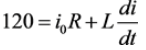
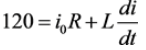
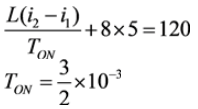
Applying KVL during TOFF,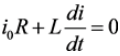
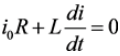
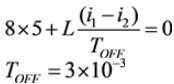
Now we can write,
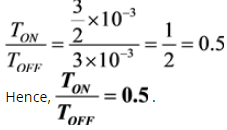

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A 120V battery supplies RL load through chopper. A freewheeling diode is connected across RL load having R=5Ω and L = 60mH. Load current varies between 7A and 9A. Calculate Ton/Toff for this chopper.Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























