Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The value of kinetic energy correction factor...
Start Learning for Free
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through...
Kinetic energy correction factor(α):
- It is defined as the ratio of kinetic energy/second based on actual velocity to the kinetic energy/second based on average velocity.
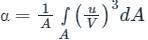
- where A = area, V= average velocity, u= local velocity at distance r.
- For laminar flow in a circular pipe α = 2
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through...
Introduction
In fluid mechanics, the kinetic energy correction factor is a dimensionless parameter that accounts for the deviation of actual flow velocity from the average velocity in a pipe. It is commonly used in the calculation of pressure drop in pipe flow.
Explanation
The kinetic energy correction factor, denoted as "C", is given by the equation:
C = (2ln(D/2r) - 1)/(ln(D/r) - 1)
where D is the pipe diameter and r is the hydraulic radius (half of the pipe diameter in the case of a circular pipe).
Derivation
To understand why the kinetic energy correction factor is 2 for laminar flow through a circular pipe, let's consider the flow profile within the pipe.
In laminar flow, the velocity distribution across the pipe is parabolic, with the maximum velocity occurring at the centerline and decreasing towards the pipe walls. The average velocity is obtained by integrating the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section.
Key Points:
- Laminar flow has a parabolic velocity profile.
- Maximum velocity occurs at the centerline.
- Average velocity is obtained by integrating the velocity profile.
Integration of the Velocity Profile
To calculate the average velocity, we need to integrate the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section. The velocity at any radial position, "r", can be given by the equation:
v(r) = (2 * Vmax) * (1 - (r/R)^2)
where Vmax is the maximum velocity at the centerline and R is the pipe radius.
Key Points:
- Velocity at any radial position, "r", is given by v(r) = (2 * Vmax) * (1 - (r/R)^2).
- Vmax is the maximum velocity at the centerline.
- R is the pipe radius.
Calculation of the Average Velocity
To calculate the average velocity, we need to integrate the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section. The integration can be performed from r = 0 to r = R, which gives:
Vavg = (2/3) * Vmax
Key Points:
- Average velocity is given by Vavg = (2/3) * Vmax.
Calculating the Kinetic Energy Correction Factor
The kinetic energy correction factor, C, is defined as the ratio of the actual kinetic energy to the kinetic energy calculated using average velocity. It can be calculated using the equation:
C = (actual kinetic energy)/(kinetic energy using average velocity)
The actual kinetic energy is given by:
KE_actual = (1/2) * ρ * Vmax^2 * (π * R^2)
The kinetic energy using average velocity is given by:
KE_avg = (1/2) * ρ * Vavg^2 * (π * R^2)
Substituting the values of Vmax and Vavg, we get:
C = (2/3)^2 = 4/9 ≈ 0.44
Key Points:
- Kinetic energy correction factor, C, is the ratio of actual kinetic energy to kinetic energy using average velocity.
- Actual kinetic energy is (1/2) * ρ * Vmax^2 * (π * R^2).
- Kinetic energy using average velocity
In fluid mechanics, the kinetic energy correction factor is a dimensionless parameter that accounts for the deviation of actual flow velocity from the average velocity in a pipe. It is commonly used in the calculation of pressure drop in pipe flow.
Explanation
The kinetic energy correction factor, denoted as "C", is given by the equation:
C = (2ln(D/2r) - 1)/(ln(D/r) - 1)
where D is the pipe diameter and r is the hydraulic radius (half of the pipe diameter in the case of a circular pipe).
Derivation
To understand why the kinetic energy correction factor is 2 for laminar flow through a circular pipe, let's consider the flow profile within the pipe.
In laminar flow, the velocity distribution across the pipe is parabolic, with the maximum velocity occurring at the centerline and decreasing towards the pipe walls. The average velocity is obtained by integrating the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section.
Key Points:
- Laminar flow has a parabolic velocity profile.
- Maximum velocity occurs at the centerline.
- Average velocity is obtained by integrating the velocity profile.
Integration of the Velocity Profile
To calculate the average velocity, we need to integrate the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section. The velocity at any radial position, "r", can be given by the equation:
v(r) = (2 * Vmax) * (1 - (r/R)^2)
where Vmax is the maximum velocity at the centerline and R is the pipe radius.
Key Points:
- Velocity at any radial position, "r", is given by v(r) = (2 * Vmax) * (1 - (r/R)^2).
- Vmax is the maximum velocity at the centerline.
- R is the pipe radius.
Calculation of the Average Velocity
To calculate the average velocity, we need to integrate the velocity profile across the pipe cross-section. The integration can be performed from r = 0 to r = R, which gives:
Vavg = (2/3) * Vmax
Key Points:
- Average velocity is given by Vavg = (2/3) * Vmax.
Calculating the Kinetic Energy Correction Factor
The kinetic energy correction factor, C, is defined as the ratio of the actual kinetic energy to the kinetic energy calculated using average velocity. It can be calculated using the equation:
C = (actual kinetic energy)/(kinetic energy using average velocity)
The actual kinetic energy is given by:
KE_actual = (1/2) * ρ * Vmax^2 * (π * R^2)
The kinetic energy using average velocity is given by:
KE_avg = (1/2) * ρ * Vavg^2 * (π * R^2)
Substituting the values of Vmax and Vavg, we get:
C = (2/3)^2 = 4/9 ≈ 0.44
Key Points:
- Kinetic energy correction factor, C, is the ratio of actual kinetic energy to kinetic energy using average velocity.
- Actual kinetic energy is (1/2) * ρ * Vmax^2 * (π * R^2).
- Kinetic energy using average velocity

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?.
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The value of kinetic energy correction factor for laminar flow through a circular pipe of radius R is _____. (Correct up to 2 decimals)Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























