Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phas...
Start Learning for Free
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)
Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is ope...
As we know in fully controlled rectifier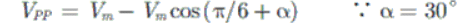
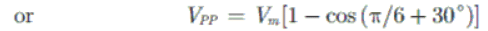
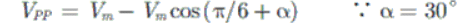
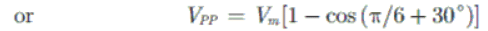
or 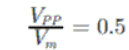
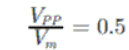
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is ope...
Introduction
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is a type of rectifier circuit used in electrical engineering. It converts AC voltage to DC voltage. The firing angle, denoted by α, determines the timing of the thyristor firing in each phase. In this case, α is given as 300 degrees.
Peak-to-Peak Voltage Ripple
The peak-to-peak voltage ripple refers to the variation in the output voltage of the rectifier. It is usually expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage. In this case, we need to calculate the peak-to-peak voltage ripple for the given firing angle of 300 degrees.
Calculating the Peak-to-Peak Voltage Ripple
To calculate the peak-to-peak voltage ripple, we can use the formula:
Vpp = (2 * √3 * Vm) / π
Where:
Vpp is the peak-to-peak voltage ripple,
Vm is the peak output DC voltage, and
π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
In this case, we are given that the firing angle α is 300 degrees. The peak output DC voltage Vm can be calculated using the formula:
Vm = √2 * Vrms
Where:
Vrms is the root mean square (RMS) voltage of the AC input.
Assuming a sinusoidal AC input voltage, the RMS voltage can be calculated as:
Vrms = Vm / √2
Therefore, Vm = Vrms * √2
Calculating Vpp
Substituting the value of Vm in the formula for Vpp, we get:
Vpp = (2 * √3 * Vm) / π
Vpp = (2 * √3 * Vrms * √2) / π
Simplifying the equation:
Vpp = (2 * √6 * Vrms) / π
Final Calculation
The ratio of the peak-to-peak voltage ripple to the peak output DC voltage is given by:
Ratio = Vpp / Vm
Substituting the values:
Ratio = [(2 * √6 * Vrms) / π] / (Vrms * √2)
Ratio = (2 * √6) / (√2 * π)
Ratio ≈ 0.5 (rounded to one decimal place)
Conclusion
The peak-to-peak voltage ripple, expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage, is approximately 0.5 for a fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier with a firing angle of 300 degrees. This means that the variation in the output voltage is half of the peak output DC voltage.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
Question Description
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A fully-controlled natural commutated 3-phase bridge rectifier is operating with a firing angle ∝ = 300. The peak to peak voltage ripple expressed as a ratio of the peak output DC voltage at the output of the converter bridge is (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















