Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A circular duct carrying water gradually con...
Start Learning for Free
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.
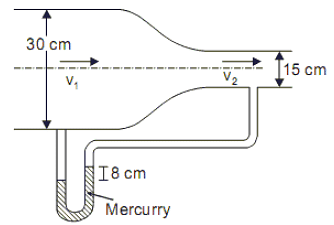
When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)
Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of...
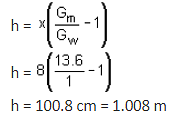
Flow rate,

A1 = 4A2 and g = 9.81 m/sec2
A2 = π/4 x 0.152
= 0.01767 m2

= 0.081 m3/sec
Most Upvoted Answer
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of...
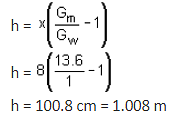
Flow rate,

A1 = 4A2 and g = 9.81 m/sec2
A2 = π/4 x 0.152
= 0.01767 m2

= 0.081 m3/sec

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer?.
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the duct is (Answer up to three decimal places)Correct answer is '0.081'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























