Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In angularity number test, the angularity num...
Start Learning for Free
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.
- a)5 to 10
- b)10 to 100
- c)0 to 11
- d)0 to 15
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used i...
Angularity:
It is the absence of roundness. An aggregate particle, which is more rounded, is less angular and vice versa.
Angularity number:
It is the absence of roundness. An aggregate particle, which is more rounded, is less angular and vice versa.
Angularity number:
- Angularity number of an aggregate is the amount (to the higher whole number) by which the percentage of voids in it after compacting in a prescribed manner exceeds 33.
- Where “33” is the percentage of the volume of voids in a perfectly rounded aggregate. And, “67” is the percentage of the volume of solids in a perfectly rounded aggregate when compacted in a specified manner.
- The value of angularity number generally lies between 0 & 11.
Determination of angularity number:
(a) From the solids
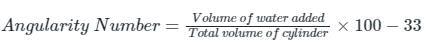
(b) From the voids
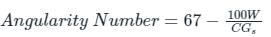
Where C = weight of the cylinder, W = weight of aggregate in the cylinder, Gs = specific gravity of aggregate
(a) From the solids
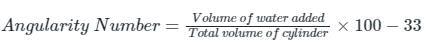
(b) From the voids
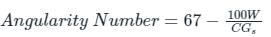
Where C = weight of the cylinder, W = weight of aggregate in the cylinder, Gs = specific gravity of aggregate
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used i...
Angularity Number Test and Angularity Number Range for Aggregates Used in Construction
The angularity number test is a method used to determine the shape and angularity of aggregates used in construction. It measures the percentage of voids in a compacted aggregate sample, which is an indication of the particle shape and surface texture. The angularity number is calculated by dividing the percentage of voids by the percentage of solid particles in the sample.
The angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from 0 to 11. This means that the percentage of voids in the compacted aggregate sample should be between 0% and 11%. Option C, "0 to 11," is the correct answer.
Why the Angularity Number Range is 0 to 11?
1. Particle Shape and Surface Texture:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number (closer to 11) have a more irregular shape and rough surface texture.
- Aggregates with a lower angularity number (closer to 0) have a more rounded shape and smooth surface texture.
- For construction purposes, aggregates with a moderate angularity number are generally preferred because they provide a good balance between stability and workability.
2. Aggregate Packing:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number tend to have better interlocking and packing characteristics.
- This can result in a more stable and durable concrete mixture.
3. Workability:
- Aggregates with a lower angularity number have better workability, which means they are easier to mix, transport, and place in concrete.
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number may require more water or additional additives to achieve the desired workability.
4. Strength and Durability:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number generally provide better strength and durability for concrete structures.
- The angularity of aggregate particles can affect the interlocking between particles and the overall mechanical properties of the concrete.
Conclusion:
In summary, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from 0 to 11. This range ensures a good balance between stability, workability, and strength in the concrete mixture. Aggregates with a moderate angularity number are preferred for most construction applications.
The angularity number test is a method used to determine the shape and angularity of aggregates used in construction. It measures the percentage of voids in a compacted aggregate sample, which is an indication of the particle shape and surface texture. The angularity number is calculated by dividing the percentage of voids by the percentage of solid particles in the sample.
The angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from 0 to 11. This means that the percentage of voids in the compacted aggregate sample should be between 0% and 11%. Option C, "0 to 11," is the correct answer.
Why the Angularity Number Range is 0 to 11?
1. Particle Shape and Surface Texture:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number (closer to 11) have a more irregular shape and rough surface texture.
- Aggregates with a lower angularity number (closer to 0) have a more rounded shape and smooth surface texture.
- For construction purposes, aggregates with a moderate angularity number are generally preferred because they provide a good balance between stability and workability.
2. Aggregate Packing:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number tend to have better interlocking and packing characteristics.
- This can result in a more stable and durable concrete mixture.
3. Workability:
- Aggregates with a lower angularity number have better workability, which means they are easier to mix, transport, and place in concrete.
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number may require more water or additional additives to achieve the desired workability.
4. Strength and Durability:
- Aggregates with a higher angularity number generally provide better strength and durability for concrete structures.
- The angularity of aggregate particles can affect the interlocking between particles and the overall mechanical properties of the concrete.
Conclusion:
In summary, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from 0 to 11. This range ensures a good balance between stability, workability, and strength in the concrete mixture. Aggregates with a moderate angularity number are preferred for most construction applications.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In angularity number test, the angularity number for aggregates used in construction generally ranges from ______.a)5 to 10b)10 to 100c)0 to 11d)0 to 15Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















