Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The ratio of horizontal stress σh to ve...
Start Learning for Free
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______
- a)coefficient of volume change
- b)coefficient of earth pressure
- c)coefficient of consolidation
- d)coefficient of compressibility
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is...
To vertical stress in a material is known as the coefficient of lateral earth pressure. This ratio can vary depending on the type of material and the specific conditions, such as the density and moisture content of the soil. In general, the coefficient of lateral earth pressure is denoted by the symbol K and can range from 0 to 1. The value of K represents the relative magnitude of the horizontal stress compared to the vertical stress.
For example, if the coefficient of lateral earth pressure is 0.5, it means that the horizontal stress is half the magnitude of the vertical stress. This indicates that the material is relatively more compressible in the horizontal direction compared to the vertical direction.
Conversely, if the coefficient of lateral earth pressure is 1, it means that the horizontal stress is equal to the vertical stress. This indicates that the material is equally compressible in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
The coefficient of lateral earth pressure is an important parameter in geotechnical engineering and is used in various calculations and analyses, such as the design of retaining walls, slope stability analysis, and foundation design.
For example, if the coefficient of lateral earth pressure is 0.5, it means that the horizontal stress is half the magnitude of the vertical stress. This indicates that the material is relatively more compressible in the horizontal direction compared to the vertical direction.
Conversely, if the coefficient of lateral earth pressure is 1, it means that the horizontal stress is equal to the vertical stress. This indicates that the material is equally compressible in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
The coefficient of lateral earth pressure is an important parameter in geotechnical engineering and is used in various calculations and analyses, such as the design of retaining walls, slope stability analysis, and foundation design.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is...
Coefficient of Earth pressure:
It is the ratio of horizontal effective stress σh and vertical effective vertical stress σv
Earth pressure at rest:
It is the ratio of horizontal effective stress σh and vertical effective vertical stress σv
Earth pressure at rest:
- It is the ratio of horizontal and vertical effective vertical stress when the retaining wall does not move at all.
- Sometimes it is also referred to as neural lateral earth pressure or lateral earth pressure
- Ko = 1−sinϕ
The coefficient of earth pressure at rest (K0) is given by,
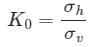
σh – Effective horizontal stress
σv – Effective vertical stress
Active earth pressure:
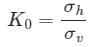
σh – Effective horizontal stress
σv – Effective vertical stress
Active earth pressure:
- It is the ratio of horizontal to vertical stress when the retaining wall moves away from the retained soil.
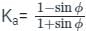
Passive earth pressure:
- It is defined as the ratio of horizontal to vertical stress when the retaining wall moves towards the retaining wall.
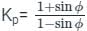

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The ratio of horizontal stress σh to vertical stress σv is ______a)coefficient of volume changeb)coefficient of earth pressurec)coefficient of consolidationd)coefficient of compressibilityCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























