Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the s...
Start Learning for Free
In Terzaghi's bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state of
- a)Plastic equilibrium
- b)Radial shear
- c)Elastic equilibrium
- d)Linear shear
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately bel...
Mechanism of Failure:
The shapes of the failure surface under ultimate loading conditions.
The zones of plastic equilibrium represented in this figure by the area may be subdivided into three zones:
1. Zone I of elastic equilibrium
2. Zones II of radial shear state
3. Zones III of Rankine passive state
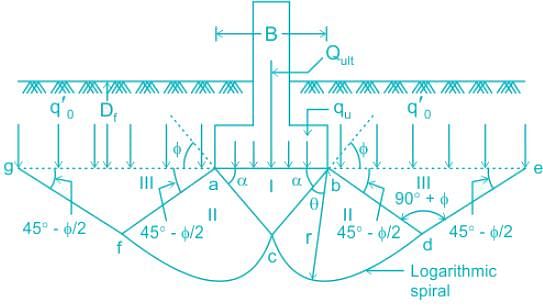
When load qu per unit area acting on the base of the footing of width B with a rough base is transmitted into the soil, the tendency of the soil located within zone I is to spread but this is counteracted by friction and adhesion between the soil and the base of the footing.
Due to the existence of this resistance against lateral spreading, the soil located immediately beneath the base remains permanently in a state of elastic equilibrium, and the soil located within this central Zone I behaves as if it were a part of the footing and sinks with the footing under the superimposed load
The shapes of the failure surface under ultimate loading conditions.
The zones of plastic equilibrium represented in this figure by the area may be subdivided into three zones:
1. Zone I of elastic equilibrium
2. Zones II of radial shear state
3. Zones III of Rankine passive state

When load qu per unit area acting on the base of the footing of width B with a rough base is transmitted into the soil, the tendency of the soil located within zone I is to spread but this is counteracted by friction and adhesion between the soil and the base of the footing.
Due to the existence of this resistance against lateral spreading, the soil located immediately beneath the base remains permanently in a state of elastic equilibrium, and the soil located within this central Zone I behaves as if it were a part of the footing and sinks with the footing under the superimposed load
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately bel...
Explanation:
Terzaghi's bearing capacity analysis is used to determine the safe load-carrying capacity of a soil foundation. It is based on the assumption that the soil below the footing is in elastic equilibrium.
Elastic Equilibrium:
In elastic equilibrium, the soil particles return to their original positions after the load is removed. This means that the soil behaves like a spring and deforms under the applied load but returns to its original shape when the load is removed.
Soil Wedge:
The soil wedge immediately below the footing refers to the soil mass that is directly in contact with the footing. It is shaped like a triangular wedge due to the shape of the footing.
Explanation of the Answer:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Elastic Equilibrium. This means that the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in a state of elastic equilibrium.
- When a load is applied to the footing, the soil wedge deforms and undergoes stress redistribution.
- The soil particles in the wedge compress and displace, causing the wedge to bulge outwards.
- However, since the soil below the footing is assumed to be in elastic equilibrium, it will return to its original shape once the load is removed.
- This assumption is valid as long as the applied load is within the safe bearing capacity of the soil.
- If the load exceeds the bearing capacity, the soil may undergo excessive deformation, leading to failure.
Significance of Elastic Equilibrium:
Assuming elastic equilibrium allows for a simplified analysis of the bearing capacity of the soil. It provides a conservative estimate of the safe load-carrying capacity of the foundation.
Note:
It is important to note that Terzaghi's bearing capacity analysis is a simplified method and does not account for all factors that can affect the bearing capacity of a soil foundation. It provides a conservative estimate and is often used as a preliminary analysis before more detailed and comprehensive analyses are conducted.
Terzaghi's bearing capacity analysis is used to determine the safe load-carrying capacity of a soil foundation. It is based on the assumption that the soil below the footing is in elastic equilibrium.
Elastic Equilibrium:
In elastic equilibrium, the soil particles return to their original positions after the load is removed. This means that the soil behaves like a spring and deforms under the applied load but returns to its original shape when the load is removed.
Soil Wedge:
The soil wedge immediately below the footing refers to the soil mass that is directly in contact with the footing. It is shaped like a triangular wedge due to the shape of the footing.
Explanation of the Answer:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Elastic Equilibrium. This means that the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in a state of elastic equilibrium.
- When a load is applied to the footing, the soil wedge deforms and undergoes stress redistribution.
- The soil particles in the wedge compress and displace, causing the wedge to bulge outwards.
- However, since the soil below the footing is assumed to be in elastic equilibrium, it will return to its original shape once the load is removed.
- This assumption is valid as long as the applied load is within the safe bearing capacity of the soil.
- If the load exceeds the bearing capacity, the soil may undergo excessive deformation, leading to failure.
Significance of Elastic Equilibrium:
Assuming elastic equilibrium allows for a simplified analysis of the bearing capacity of the soil. It provides a conservative estimate of the safe load-carrying capacity of the foundation.
Note:
It is important to note that Terzaghi's bearing capacity analysis is a simplified method and does not account for all factors that can affect the bearing capacity of a soil foundation. It provides a conservative estimate and is often used as a preliminary analysis before more detailed and comprehensive analyses are conducted.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In Terzaghis bearing capacity analysis, the soil wedge immediately below the footing remains in state ofa)Plastic equilibriumb)Radial shearc)Elastic equilibriumd)Linear shearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























