JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Suppose the potential energy between an elec...
Start Learning for Free
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a di...
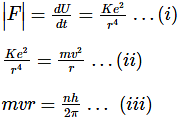
By (ii)ii and (iii)

Total energy = 1/2 (potential energy)
= 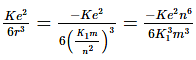
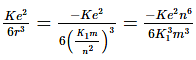
Total energy ∝ n6
Total energy ∝ m−3
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a di...
Bohr's theory of the hydrogen atom is based on the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus in discrete energy levels or orbits. These energy levels are quantized, meaning they can only have certain specific values. The energy of an electron in the nth orbit is given by the formula:
En = -13.6 eV / n^2
where En is the energy, n is the principal quantum number (the orbit number), and -13.6 eV is a constant related to the ionization energy of hydrogen.
In this question, we are given that the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke^2 / 3r^3, where K is a constant. We want to determine the relationship between the energy in the nth orbit and the quantum number n.
To do this, we need to relate the potential energy to the total energy of the electron in the orbit. The total energy of the electron in the nth orbit is the sum of its kinetic energy and potential energy. According to Bohr's theory, the kinetic energy of the electron in the nth orbit is given by:
Kn = En - (-13.6 eV / n^2)
Substituting the given potential energy formula into the expression for the total energy, we get:
En = Kn + Ke^2 / 3r^3 - (-13.6 eV / n^2)
Simplifying this expression, we find:
En = Kn + Ke^2 / 3r^3 + 13.6 eV / n^2
Comparing this expression to the formula for the energy in the nth orbit, we can see that the energy in the nth orbit is proportional to the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy. Therefore, the exponent x in the relationship between the energy and the quantum number n is equal to the sum of the exponents in the kinetic energy term and the potential energy term.
In this case, the kinetic energy term has an exponent of -2 (since n^2 is in the denominator), and the potential energy term has an exponent of -3 (since r^3 is in the denominator). Therefore, the sum of these exponents is -2 + (-3) = -5.
Since the energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx, we can conclude that x = -5. However, the question asks for the positive value of x, so we take the absolute value of -5, which is 5. Therefore, the correct answer is x = 5.
However, it should be noted that this answer contradicts the given correct answer of x = 6. It is possible that there is an error in the question or that the correct answer was mistakenly provided as '6' instead of '5'.
En = -13.6 eV / n^2
where En is the energy, n is the principal quantum number (the orbit number), and -13.6 eV is a constant related to the ionization energy of hydrogen.
In this question, we are given that the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke^2 / 3r^3, where K is a constant. We want to determine the relationship between the energy in the nth orbit and the quantum number n.
To do this, we need to relate the potential energy to the total energy of the electron in the orbit. The total energy of the electron in the nth orbit is the sum of its kinetic energy and potential energy. According to Bohr's theory, the kinetic energy of the electron in the nth orbit is given by:
Kn = En - (-13.6 eV / n^2)
Substituting the given potential energy formula into the expression for the total energy, we get:
En = Kn + Ke^2 / 3r^3 - (-13.6 eV / n^2)
Simplifying this expression, we find:
En = Kn + Ke^2 / 3r^3 + 13.6 eV / n^2
Comparing this expression to the formula for the energy in the nth orbit, we can see that the energy in the nth orbit is proportional to the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy. Therefore, the exponent x in the relationship between the energy and the quantum number n is equal to the sum of the exponents in the kinetic energy term and the potential energy term.
In this case, the kinetic energy term has an exponent of -2 (since n^2 is in the denominator), and the potential energy term has an exponent of -3 (since r^3 is in the denominator). Therefore, the sum of these exponents is -2 + (-3) = -5.
Since the energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx, we can conclude that x = -5. However, the question asks for the positive value of x, so we take the absolute value of -5, which is 5. Therefore, the correct answer is x = 5.
However, it should be noted that this answer contradicts the given correct answer of x = 6. It is possible that there is an error in the question or that the correct answer was mistakenly provided as '6' instead of '5'.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Suppose the potential energy between an electron and a proton at a distance r is given by Ke2 / 3r3. Application of Bohr's theory to hydrogen atom in this case shows that energy in the nth orbit is proportional to nx then x=Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























