Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Which of the following magnetic materials hav...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?
- a)Saturable magnetic material
- b)Soft magnetic material
- c)Hard magnetic material
- d)Diamagnetic material
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresi...
Soft magnetic materials have a small area of the hysteresis loop.
Hysteresis Loop (B.H Curve):
Hysteresis Loop (B.H Curve):
- Consider a completely demagnetized ferromagnetic material (i.e. B = H = 0)
- It will be subjected to the increasing value of magnetic field strength (H) and the corresponding flux density (B) measured the result is shown in the below figure by the curve O-a-b.
- At point b, if the field intensity (H) is increased further the flux density (B’) will not increase anymore, this is called saturation b-y is called solution flux density.
- Now if field intensity (H) is decreased, the flux density (B) will follow the curve b-c. When field intensity (H) is reduced to zero, flux remains the iron this is called remanent flux density or remanence, it is shown in fig. O-C.
- Now if the H increased in the opposite direction the flux density decreases until the point d here the flux density (B) is zero.
- The magnetic field strength (points between O and d) require to remove the residual magnetism i.e. reduce B to zero called a coercive force.
- Now if H is increased further in the reverse direction causes the flux density to increase in the reverse direction all the saturation point e.
- If H is varied backwords OX to O-Y, the flux Density (B) follows the curve b-c-d-d.
- From the figure the clear that flux density changes ‘log behind the changes in the magnetic field strength this effect is called hysteresis.
- The closed figure b-c-d-e-f-g-b is called the hysteresis loop.
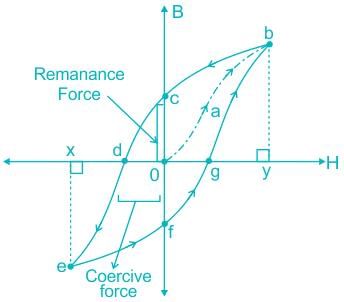
- The energy loss associated with hysteresis is proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop.
- The area of the hysteresis loop varies with the type of material.
- For hard material: hysteresis loop area large → hysteresis loss also more → high remanence (O-C) and large coercivity (O-d).
- For soft material: hysteresis loop area small → hysteresis loss less → large remanence and small coercivity.
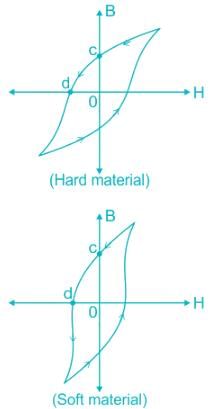
Note:
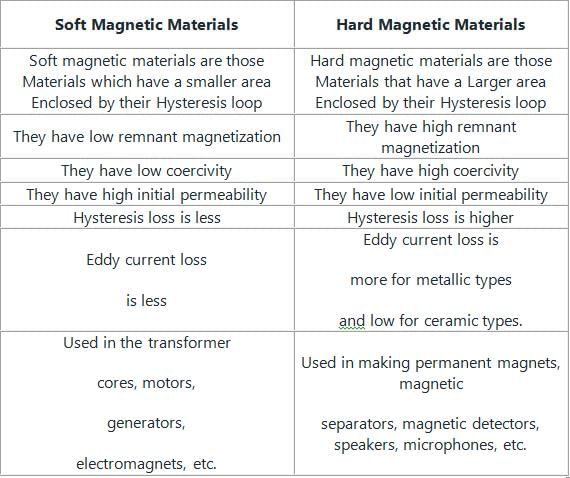
The difference between soft magnetic materials & hard magnetic materials is as shown:
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresi...
Soft magnetic material
Soft magnetic materials have a small area of hysteresis loop compared to hard magnetic materials. This is due to their ability to magnetize and demagnetize easily, making them ideal for applications where frequent magnetic changes are required.
Reasons for small area of hysteresis loop in soft magnetic materials:
- Soft magnetic materials have high permeability, which means they can easily accommodate changes in magnetic field without retaining magnetization.
- These materials have low coercivity, allowing them to quickly switch between magnetized states.
- Soft magnetic materials have a narrow hysteresis loop, indicating low energy loss during magnetization cycles.
Applications of soft magnetic materials:
- Transformers: Soft magnetic materials are used in transformer cores to efficiently transfer energy between circuits.
- Inductors: These materials are also used in inductors to store and release energy in electronic circuits.
- Electric motors: Soft magnetic materials play a crucial role in the operation of electric motors by enabling rapid changes in magnetic fields.
In conclusion, soft magnetic materials exhibit a small area of hysteresis loop due to their high permeability, low coercivity, and efficient magnetization properties. Their unique characteristics make them essential in various electrical and electronic applications.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following magnetic materials have small area of hysteresis loop?a)Saturable magnetic materialb)Soft magnetic materialc)Hard magnetic materiald)Diamagnetic materialCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























