Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results...
Start Learning for Free
The 'Sag' in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:
- a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the stream
- b)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the stream
- c)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the stream
- d)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linear
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a functi...
Oxygen sag curve of river manifest dissolved oxygen deficit.
The difference between saturated dissolved oxygen content and the actual dissolved oxygen content in the stream at any point during self-purification process is called Oxygen sag
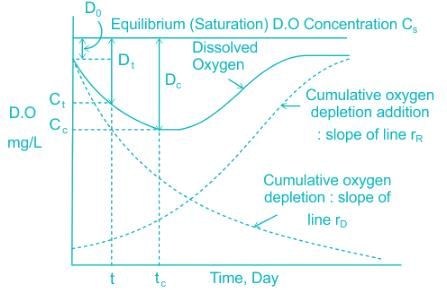
Oxygen sag curve or oxygen deficit curve is obtained by algebraic addition of deoxygenation and reoxygenation curve.
The difference between saturated dissolved oxygen content and the actual dissolved oxygen content in the stream at any point during self-purification process is called Oxygen sag

Oxygen sag curve or oxygen deficit curve is obtained by algebraic addition of deoxygenation and reoxygenation curve.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a functi...
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because it is a function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the stream.
Explanation:
1. Dissolved Oxygen Curve:
The dissolved oxygen (DO) curve is a graphical representation of the concentration of oxygen dissolved in water over a certain period of time. It is commonly used to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems and to monitor water quality.
2. Rate of Addition of Oxygen:
The rate of addition of oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen that is being introduced into the stream. This can occur through various natural processes such as diffusion from the atmosphere, photosynthesis by aquatic plants, or artificial means such as aeration devices.
3. Rate of Depletion of Oxygen:
The rate of depletion of oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen that is being consumed or removed from the stream. This can occur due to biological processes such as respiration by aquatic organisms, decomposition of organic matter, or physical processes such as mixing and turbulence.
4. Relationship between Addition and Depletion:
The dissolved oxygen concentration in a stream is influenced by both the rate of addition and the rate of depletion of oxygen. When the rate of addition exceeds the rate of depletion, the dissolved oxygen concentration increases, resulting in an upward trend in the DO curve. Conversely, when the rate of depletion exceeds the rate of addition, the dissolved oxygen concentration decreases, resulting in a downward trend in the DO curve.
5. The Sag in the DO Curve:
The sag in the dissolved oxygen curve occurs when the rate of depletion of oxygen starts to exceed the rate of addition. This can happen when there is a high demand for oxygen due to increased biological activity or when the rate of addition is reduced due to factors such as reduced atmospheric oxygen exchange or pollution.
6. Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Option C is the correct answer because the sag in the dissolved oxygen curve is a result of both the rate of addition and the rate of depletion of oxygen from the stream. It is the point where the rate of depletion exceeds the rate of addition, leading to a decrease in dissolved oxygen concentration.
In summary, the sag in the dissolved oxygen curve occurs when the rate of depletion of oxygen exceeds the rate of addition. It is an important indicator of the health and quality of aquatic ecosystems, and understanding the factors influencing the sag can help in the assessment and management of water resources.
Explanation:
1. Dissolved Oxygen Curve:
The dissolved oxygen (DO) curve is a graphical representation of the concentration of oxygen dissolved in water over a certain period of time. It is commonly used to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems and to monitor water quality.
2. Rate of Addition of Oxygen:
The rate of addition of oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen that is being introduced into the stream. This can occur through various natural processes such as diffusion from the atmosphere, photosynthesis by aquatic plants, or artificial means such as aeration devices.
3. Rate of Depletion of Oxygen:
The rate of depletion of oxygen refers to the amount of oxygen that is being consumed or removed from the stream. This can occur due to biological processes such as respiration by aquatic organisms, decomposition of organic matter, or physical processes such as mixing and turbulence.
4. Relationship between Addition and Depletion:
The dissolved oxygen concentration in a stream is influenced by both the rate of addition and the rate of depletion of oxygen. When the rate of addition exceeds the rate of depletion, the dissolved oxygen concentration increases, resulting in an upward trend in the DO curve. Conversely, when the rate of depletion exceeds the rate of addition, the dissolved oxygen concentration decreases, resulting in a downward trend in the DO curve.
5. The Sag in the DO Curve:
The sag in the dissolved oxygen curve occurs when the rate of depletion of oxygen starts to exceed the rate of addition. This can happen when there is a high demand for oxygen due to increased biological activity or when the rate of addition is reduced due to factors such as reduced atmospheric oxygen exchange or pollution.
6. Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Option C is the correct answer because the sag in the dissolved oxygen curve is a result of both the rate of addition and the rate of depletion of oxygen from the stream. It is the point where the rate of depletion exceeds the rate of addition, leading to a decrease in dissolved oxygen concentration.
In summary, the sag in the dissolved oxygen curve occurs when the rate of depletion of oxygen exceeds the rate of addition. It is an important indicator of the health and quality of aquatic ecosystems, and understanding the factors influencing the sag can help in the assessment and management of water resources.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The Sag in the dissolved oxygen curve results because:a)it is a function of the rate of addition of oxygen to the streamb)it is a function of the rate of depletion of oxygen from the streamc)it is function of the rate of both addition and depletion of oxygen from the streamd)the rate of addition of oxygen is linear but the rate of depletion of oxygen is non-linearCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























