Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Questions > In context of error detection and correction ...
Start Learning for Free
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:
- a)Cyclic Reduction Code
- b)Cyclic Redundancy Check
- c)Cyber Request Check
- d)Cyber Repetition Code
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC...
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
CRC stands for Cyclic Redundancy Check and is a method used for error detection in computer networks. It is widely used in communication protocols, such as Ethernet, to ensure the integrity of transmitted data.
How CRC Works
CRC involves the use of a polynomial division algorithm to generate a checksum for a block of data. This checksum is appended to the data and transmitted along with it. At the receiving end, the same polynomial division algorithm is applied to the received data, including the checksum. If the calculated checksum matches the received checksum, it indicates that the data has been received without errors. However, if the checksums do not match, it suggests that errors have occurred during transmission.
Polynomial Division Algorithm
The polynomial division algorithm used in CRC involves treating the data as a string of bits and dividing it by a predetermined divisor polynomial. The divisor polynomial is typically represented as a binary number and is chosen based on the specific CRC algorithm being used. The division process is performed bit by bit, with each bit being exclusive-ORed (XOR) with the corresponding bit of the divisor. The result of this XOR operation determines whether the next bit of the data should be XORed with the divisor or not. This process continues until all bits of the data have been processed.
Checksum Calculation
The CRC checksum is calculated by performing the polynomial division algorithm on the data, including the appended checksum bits. The remainder obtained from this division is the checksum. The checksum is then appended to the original data and transmitted.
Error Detection
At the receiving end, the same polynomial division algorithm is applied to the received data, including the appended checksum. If the remainder obtained from the division is zero, it indicates that no errors have occurred during transmission. However, if the remainder is non-zero, it suggests that errors have occurred.
Conclusion
CRC is a powerful error detection technique used in computer networks to ensure the integrity of transmitted data. By calculating a checksum using a polynomial division algorithm, CRC can detect errors introduced during transmission. It is a widely used and efficient method for error detection in various communication protocols.
CRC stands for Cyclic Redundancy Check and is a method used for error detection in computer networks. It is widely used in communication protocols, such as Ethernet, to ensure the integrity of transmitted data.
How CRC Works
CRC involves the use of a polynomial division algorithm to generate a checksum for a block of data. This checksum is appended to the data and transmitted along with it. At the receiving end, the same polynomial division algorithm is applied to the received data, including the checksum. If the calculated checksum matches the received checksum, it indicates that the data has been received without errors. However, if the checksums do not match, it suggests that errors have occurred during transmission.
Polynomial Division Algorithm
The polynomial division algorithm used in CRC involves treating the data as a string of bits and dividing it by a predetermined divisor polynomial. The divisor polynomial is typically represented as a binary number and is chosen based on the specific CRC algorithm being used. The division process is performed bit by bit, with each bit being exclusive-ORed (XOR) with the corresponding bit of the divisor. The result of this XOR operation determines whether the next bit of the data should be XORed with the divisor or not. This process continues until all bits of the data have been processed.
Checksum Calculation
The CRC checksum is calculated by performing the polynomial division algorithm on the data, including the appended checksum bits. The remainder obtained from this division is the checksum. The checksum is then appended to the original data and transmitted.
Error Detection
At the receiving end, the same polynomial division algorithm is applied to the received data, including the appended checksum. If the remainder obtained from the division is zero, it indicates that no errors have occurred during transmission. However, if the remainder is non-zero, it suggests that errors have occurred.
Conclusion
CRC is a powerful error detection technique used in computer networks to ensure the integrity of transmitted data. By calculating a checksum using a polynomial division algorithm, CRC can detect errors introduced during transmission. It is a widely used and efficient method for error detection in various communication protocols.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC...
A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to raw data. Blocks of data entering these systems get a short check value attached, based on the remainder of a polynomial division of their contents.
Example
Polynomial is: x5 + x4 + x2 +1
A polynomial higher degree is 5, so append 5 0’s to the message bits.
Message: 1010001101 00000
Divisor polynomial in bits = 110101
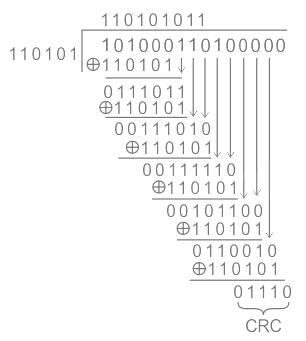
Example
Polynomial is: x5 + x4 + x2 +1
A polynomial higher degree is 5, so append 5 0’s to the message bits.
Message: 1010001101 00000
Divisor polynomial in bits = 110101


|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In context of error detection and correction in computer networks, CRC stands for:a)Cyclic Reduction Codeb)Cyclic Redundancy Checkc)Cyber Request Checkd)Cyber Repetition CodeCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Computer Science Engineering (CSE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















