Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The drag and lift forces experienced by an ob...
Start Learning for Free
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due to
- a)Pressure and turbulence
- b)Viscosity and turbulence
- c)Pressure and viscosity
- d)Pressure and gravity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid st...
Concept: -
When a body is immersed in the fluid under motion, it subjected to Drag and lift forces, this is due to pressure and viscosity.
Drag Force: - It is the horizontal component of the force exerted by the fluid around the body when it is immersed in a fluid under motion. It has two components pressure drag and friction drag. It is given by –
When a body is immersed in the fluid under motion, it subjected to Drag and lift forces, this is due to pressure and viscosity.
Drag Force: - It is the horizontal component of the force exerted by the fluid around the body when it is immersed in a fluid under motion. It has two components pressure drag and friction drag. It is given by –
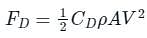
- Friction Drag is also known as Skin Friction Drag.
- The drag on a body resulting from viscous shearing stresses over its contact surface.
- It is directly proportional to the area of the surface in contact with the fluid and increases with the square of the velocity
- The drag of a very streamlined shape such as a thin, flat plate is frequently expressed in terms of a skin friction drag.
Lift force: - It is the vertical component of the force exerted by the fluid around the body when it is immersed in a fluid under motion. It is given by –


- Lift forces acts due to the pressure difference between the top and bottom surface of the plate or body.
- If the axis of the body is parallel to the direction of fluid flow the lift force is zero and only drag force acts.
Here,
CL and CD – Coefficient of lift and drag force respectively.
A – a maximum projected area of the body (m2)
ρ – density of fluid (kg/m3)
V – average velocity of stream (m/sec)
Note: - If fluid is assumed to be ideal (Non viscous) and body is symmetrical such as sphere or cylinder, Both drag and lift force will be zero.
CL and CD – Coefficient of lift and drag force respectively.
A – a maximum projected area of the body (m2)
ρ – density of fluid (kg/m3)
V – average velocity of stream (m/sec)
Note: - If fluid is assumed to be ideal (Non viscous) and body is symmetrical such as sphere or cylinder, Both drag and lift force will be zero.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid st...
Drag and Lift Forces in Fluid Flow
Introduction:
When an object is placed in a fluid stream, such as air or water, it experiences forces known as drag and lift forces. These forces are crucial in understanding the behavior of objects moving through fluids and have significant implications in various fields, including civil engineering.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option C, which states that the drag and lift forces experienced by an object in a fluid stream are due to pressure and viscosity. Let's understand this in detail:
1. Pressure:
- Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit area of a surface. In fluid flow, pressure is distributed unevenly around an object due to the variation in fluid velocity.
- When an object moves through a fluid stream, the fluid particles in front of the object get compressed, leading to an increase in pressure.
- On the other hand, the fluid particles behind the object experience lower pressure due to the expansion of the fluid stream.
- This difference in pressure creates a force known as drag, which acts in the opposite direction to the motion of the object.
- Drag force is directly proportional to the pressure difference and the surface area of the object facing the fluid stream.
2. Viscosity:
- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It determines the internal friction within the fluid.
- When an object moves through a fluid stream, the fluid particles in contact with the object's surface experience shear stress due to the difference in velocities between the object and the fluid.
- This shear stress causes the fluid to flow in layers, with the fluid near the object's surface moving slower than the fluid away from the surface.
- The velocity gradient within the fluid creates a force known as viscous drag or skin friction, which opposes the motion of the object.
- Viscous drag force is directly proportional to the viscosity of the fluid, the surface area of the object, and the velocity gradient.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are primarily due to pressure and viscosity. Pressure variations around the object create the drag force, while the internal friction caused by viscosity leads to the viscous drag force. Understanding these forces is essential in designing structures to withstand fluid flow, such as bridges, dams, and offshore structures.
Introduction:
When an object is placed in a fluid stream, such as air or water, it experiences forces known as drag and lift forces. These forces are crucial in understanding the behavior of objects moving through fluids and have significant implications in various fields, including civil engineering.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option C, which states that the drag and lift forces experienced by an object in a fluid stream are due to pressure and viscosity. Let's understand this in detail:
1. Pressure:
- Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit area of a surface. In fluid flow, pressure is distributed unevenly around an object due to the variation in fluid velocity.
- When an object moves through a fluid stream, the fluid particles in front of the object get compressed, leading to an increase in pressure.
- On the other hand, the fluid particles behind the object experience lower pressure due to the expansion of the fluid stream.
- This difference in pressure creates a force known as drag, which acts in the opposite direction to the motion of the object.
- Drag force is directly proportional to the pressure difference and the surface area of the object facing the fluid stream.
2. Viscosity:
- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It determines the internal friction within the fluid.
- When an object moves through a fluid stream, the fluid particles in contact with the object's surface experience shear stress due to the difference in velocities between the object and the fluid.
- This shear stress causes the fluid to flow in layers, with the fluid near the object's surface moving slower than the fluid away from the surface.
- The velocity gradient within the fluid creates a force known as viscous drag or skin friction, which opposes the motion of the object.
- Viscous drag force is directly proportional to the viscosity of the fluid, the surface area of the object, and the velocity gradient.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are primarily due to pressure and viscosity. Pressure variations around the object create the drag force, while the internal friction caused by viscosity leads to the viscous drag force. Understanding these forces is essential in designing structures to withstand fluid flow, such as bridges, dams, and offshore structures.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due toa)Pressure and turbulenceb)Viscosity and turbulencec)Pressure and viscosityd)Pressure and gravityCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























