Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at...
Start Learning for Free
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is called
- a)Semiconfined aquifer
- b)Unconfined aquifer
- c)Confined aquifer
- d)Perched aquifer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semic...
**Unconfined Aquifer**
An aquifer is a geological formation that contains and transmits groundwater. It can be classified based on its hydraulic properties and the geological formations surrounding it. One such classification is based on its confinement, which refers to the ability of the aquifer to transmit water.
An unconfined aquifer is a type of aquifer that is not confined at the top. It is also known as a water table aquifer. This means that the water table, which is the upper surface of the groundwater, is free to rise and fall based on natural processes such as rainfall and evaporation. The water in an unconfined aquifer is under atmospheric pressure.
**Characteristics of an Unconfined Aquifer:**
1. **No Upper Confining Layer:** In an unconfined aquifer, there is no impermeable layer of rock or soil above the water table. This allows precipitation to infiltrate through the surface and recharge the aquifer. It also means that the water table is in direct contact with the atmosphere.
2. **Water Table Fluctuations:** The water table in an unconfined aquifer can rise and fall depending on the balance between recharge and discharge. During periods of heavy rainfall or recharge, the water table may rise, while during dry periods or excessive pumping, the water table may decline.
3. **Vulnerable to Contamination:** Because there is no confining layer at the top, unconfined aquifers are more susceptible to contamination from surface pollutants. Pollutants can easily infiltrate through the unsaturated zone and reach the water table, potentially impacting the quality of the groundwater.
4. **Ease of Access:** Since there is no confining layer, it is relatively easier to access water from an unconfined aquifer compared to a confined aquifer. Wells can be drilled directly into the water table, allowing for the extraction of water for various purposes, such as irrigation or domestic use.
In summary, an unconfined aquifer is a type of aquifer that is not confined at the top. It is characterized by a fluctuating water table, vulnerability to contamination, and relatively easy access to groundwater.
An aquifer is a geological formation that contains and transmits groundwater. It can be classified based on its hydraulic properties and the geological formations surrounding it. One such classification is based on its confinement, which refers to the ability of the aquifer to transmit water.
An unconfined aquifer is a type of aquifer that is not confined at the top. It is also known as a water table aquifer. This means that the water table, which is the upper surface of the groundwater, is free to rise and fall based on natural processes such as rainfall and evaporation. The water in an unconfined aquifer is under atmospheric pressure.
**Characteristics of an Unconfined Aquifer:**
1. **No Upper Confining Layer:** In an unconfined aquifer, there is no impermeable layer of rock or soil above the water table. This allows precipitation to infiltrate through the surface and recharge the aquifer. It also means that the water table is in direct contact with the atmosphere.
2. **Water Table Fluctuations:** The water table in an unconfined aquifer can rise and fall depending on the balance between recharge and discharge. During periods of heavy rainfall or recharge, the water table may rise, while during dry periods or excessive pumping, the water table may decline.
3. **Vulnerable to Contamination:** Because there is no confining layer at the top, unconfined aquifers are more susceptible to contamination from surface pollutants. Pollutants can easily infiltrate through the unsaturated zone and reach the water table, potentially impacting the quality of the groundwater.
4. **Ease of Access:** Since there is no confining layer, it is relatively easier to access water from an unconfined aquifer compared to a confined aquifer. Wells can be drilled directly into the water table, allowing for the extraction of water for various purposes, such as irrigation or domestic use.
In summary, an unconfined aquifer is a type of aquifer that is not confined at the top. It is characterized by a fluctuating water table, vulnerability to contamination, and relatively easy access to groundwater.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semic...
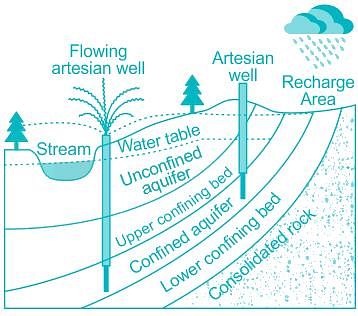
Unconfined aquifer:
- An unconfined aquifers is one in which the water table forms the upper surface of zone of saturation.
- The term unconfined signifies the absence of any geological layer confining the zone of saturation (above the water table).
- The unconfined aquifer is in direct contact with atmosphere through the zone of aeration. At the water table, the hydraulic pressure head or ground water pressure head is equal to atmospheric pressure (i.e. zero).
- This aquifer is also known as water table aquifer or phreatic aquifer.
Confined aquifer:
- The confined aquifer a geological formation qualifying as an aquifer is overlained by a impermeable layer or an aquiclude.
- The confining layers show very low intrinsic permeability (k).Here the overlying layer acts as layer confining the underlying aquifer.
- The water in the confined aquifer is not in direct contact with the
atmosphere. This is because of the presence of confining layer overlying the confined aquifer.
Semiconfined aquifer:
- An aquifer partially confined by soil layers of low permeability through which recharge and discharge can still occur.
- Semi-confined aquifers can usually be located between aquifers and the ground surface with the water seeping into via the internal layers to move freely through the main aquifers.
Perched aquifer:
- A special case of unconfined aquifer is known as perched aquifer. A perched aquifer is formed when the infiltrated rain water is intercepted within the zone of Aeration by an impermeable layer and a local zone of saturation is formed.
- The upper surface of such local zone of saturation is known as perched water table. The perched aquifer occurs at higher elevation than the regional water table.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An aquifer confined at the bottom, but NOT at the top is calleda)Semiconfined aquiferb)Unconfined aquiferc)Confined aquiferd)Perched aquiferCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























