Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT c...
Start Learning for Free
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?
- a)Ideal fluid
- b)Real fluid
- c)Newtonian fluid
- d)Non-Newtonian fluid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of de...
Newtonian fluid is the fluid whose viscosity does not change with the rate of deformation. Let's understand this concept in detail.
Definition of Newtonian Fluid:
A Newtonian fluid is a type of fluid where the shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain. In other words, the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid remains constant regardless of the rate of deformation or shear rate.
Explanation:
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. In most fluids, the viscosity changes with the rate of deformation. However, in the case of Newtonian fluids, the viscosity remains constant at all shear rates. This means that the fluid's behavior does not change whether it is sheared quickly or slowly.
The behavior of Newtonian fluids can be described by Newton's law of viscosity, which states that the shear stress (τ) is directly proportional to the velocity gradient (du/dy) in the direction perpendicular to the flow.
τ = μ (du/dy)
Where:
- τ is the shear stress
- μ is the dynamic viscosity
- (du/dy) is the velocity gradient
Key Characteristics of Newtonian Fluids:
1. Constant viscosity: The most important characteristic of Newtonian fluids is that their viscosity remains constant regardless of the shear rate or rate of deformation.
2. Linear relationship between shear stress and shear rate: Newtonian fluids exhibit a linear relationship between shear stress and shear rate, as described by Newton's law of viscosity.
3. Examples of Newtonian fluids: Some common examples of Newtonian fluids include water, air, gasoline, and most oils.
Importance in Engineering:
The concept of Newtonian fluids is widely used in engineering applications. It helps engineers predict and analyze the flow behavior of fluids in various systems, such as pipes, channels, and pumps. Understanding the constant viscosity of Newtonian fluids is crucial for designing efficient systems and ensuring proper fluid flow.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a Newtonian fluid is the type of fluid whose viscosity remains constant regardless of the rate of deformation or shear rate. This characteristic makes it distinct from other types of fluids, such as non-Newtonian fluids, which exhibit variable viscosity with changing shear rates.
Definition of Newtonian Fluid:
A Newtonian fluid is a type of fluid where the shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain. In other words, the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid remains constant regardless of the rate of deformation or shear rate.
Explanation:
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. In most fluids, the viscosity changes with the rate of deformation. However, in the case of Newtonian fluids, the viscosity remains constant at all shear rates. This means that the fluid's behavior does not change whether it is sheared quickly or slowly.
The behavior of Newtonian fluids can be described by Newton's law of viscosity, which states that the shear stress (τ) is directly proportional to the velocity gradient (du/dy) in the direction perpendicular to the flow.
τ = μ (du/dy)
Where:
- τ is the shear stress
- μ is the dynamic viscosity
- (du/dy) is the velocity gradient
Key Characteristics of Newtonian Fluids:
1. Constant viscosity: The most important characteristic of Newtonian fluids is that their viscosity remains constant regardless of the shear rate or rate of deformation.
2. Linear relationship between shear stress and shear rate: Newtonian fluids exhibit a linear relationship between shear stress and shear rate, as described by Newton's law of viscosity.
3. Examples of Newtonian fluids: Some common examples of Newtonian fluids include water, air, gasoline, and most oils.
Importance in Engineering:
The concept of Newtonian fluids is widely used in engineering applications. It helps engineers predict and analyze the flow behavior of fluids in various systems, such as pipes, channels, and pumps. Understanding the constant viscosity of Newtonian fluids is crucial for designing efficient systems and ensuring proper fluid flow.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a Newtonian fluid is the type of fluid whose viscosity remains constant regardless of the rate of deformation or shear rate. This characteristic makes it distinct from other types of fluids, such as non-Newtonian fluids, which exhibit variable viscosity with changing shear rates.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of de...
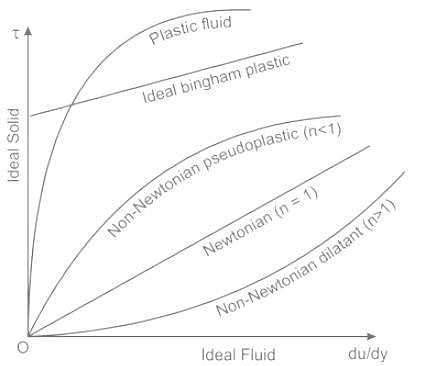
Newtonian fluids: fluids for which the shear stress is linearly proportional to the shear strain rate and follow Newton's law of viscosity.
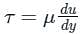 where μ is shear viscosity of the fluid
where μ is shear viscosity of the fluid- Newtonian fluids are analogous to elastic solids (Hooke’s law: stress proportional to strain)
- Any common fluids, such as air and other gases, water, kerosene, gasoline, and other oil-based liquids, are Newtonian fluids
- A fluid whose viscosity does not change with the rate of deformation or shear strain is known as a Newtonian fluid.
Non-Newtonian fluid: fluids for which the shear stress is not linearly related to the shear strain rate are called non-Newtonian fluids
- In non-Newtonian, the viscosity is dependent on the shear rate (Shear Thinning or Thickening)
- examples include slurries and colloidal suspensions, polymer solutions, blood, paste, and cake batter
Ideal fluid: fluids which don’t have viscosity and are incompressible are termed as an ideal fluid
- The ideal fluid does not offer shear resistance i.e no resistance is encountered as the fluid moves.
Real fluid: fluids which do possess viscosity are termed as real fluids.
- These fluids always offer shear resistance i.e. Certain amount of resistance is always offered by these fluids as they move.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which is the fluid whose viscosity does NOT change with the rate of deformation?a)Ideal fluidb)Real fluidc)Newtonian fluidd)Non-Newtonian fluidCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























