Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stok...
Start Learning for Free
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will be
- a)0.33 m/s
- b)0.66 m/s
- c)2 m/s
- d)6 m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of ...
To understand the given problem, we need to apply the concept of dynamic similarity. Dynamic similarity refers to the similarity in the flow characteristics between two different fluids or situations. In this case, we are comparing the flow of water and oil in pipes of the same diameter.
Given data:
- Kinematic viscosity of water (ν1) = 0.01 stoke
- Velocity of water (V1) = 2 m/s
- Diameter of the pipe (D) = 15 cm
We need to find the velocity of oil (V2) in a pipe of the same diameter, but with a different kinematic viscosity (ν2 = 0.03 stoke).
The concept of dynamic similarity is based on the Reynolds number (Re), which is a dimensionless quantity that determines the flow regime. It is given by the formula:
Re = (ρ * V * D) / μ
where:
- ρ is the density of the fluid
- V is the velocity of the fluid
- D is the diameter of the pipe
- μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid
In this case, we can assume that the density of water and oil are approximately the same, so we can neglect the density term. Now, let's calculate the Reynolds number for water:
Re1 = (ρ * V1 * D) / μ1
Similarly, let's calculate the Reynolds number for oil:
Re2 = (ρ * V2 * D) / μ2
As per the concept of dynamic similarity, the Reynolds number should be the same for both fluids in order to have similar flow characteristics. Therefore, we can set up the following equation:
Re1 = Re2
Substituting the values, we get:
(ρ * V1 * D) / μ1 = (ρ * V2 * D) / μ2
Canceling out the common terms and rearranging the equation, we get:
V2 = (V1 * μ2) / μ1
Now, substituting the given values:
V2 = (2 * 0.03) / 0.01 = 6 m/s
Hence, the velocity of oil in a pipe of the same diameter will be 6 m/s (option D).
Given data:
- Kinematic viscosity of water (ν1) = 0.01 stoke
- Velocity of water (V1) = 2 m/s
- Diameter of the pipe (D) = 15 cm
We need to find the velocity of oil (V2) in a pipe of the same diameter, but with a different kinematic viscosity (ν2 = 0.03 stoke).
The concept of dynamic similarity is based on the Reynolds number (Re), which is a dimensionless quantity that determines the flow regime. It is given by the formula:
Re = (ρ * V * D) / μ
where:
- ρ is the density of the fluid
- V is the velocity of the fluid
- D is the diameter of the pipe
- μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid
In this case, we can assume that the density of water and oil are approximately the same, so we can neglect the density term. Now, let's calculate the Reynolds number for water:
Re1 = (ρ * V1 * D) / μ1
Similarly, let's calculate the Reynolds number for oil:
Re2 = (ρ * V2 * D) / μ2
As per the concept of dynamic similarity, the Reynolds number should be the same for both fluids in order to have similar flow characteristics. Therefore, we can set up the following equation:
Re1 = Re2
Substituting the values, we get:
(ρ * V1 * D) / μ1 = (ρ * V2 * D) / μ2
Canceling out the common terms and rearranging the equation, we get:
V2 = (V1 * μ2) / μ1
Now, substituting the given values:
V2 = (2 * 0.03) / 0.01 = 6 m/s
Hence, the velocity of oil in a pipe of the same diameter will be 6 m/s (option D).
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of ...
Concept
For Dynamic similarity the ratio of corresponding forces acting at the corresponding points should be the same in the model and prototype, the ratio of these forces are called dimensionless numbers.
Therefore for the dynamic similarity between the model and prototype the dimensionless should also be the same. The models are designed on the basis of dominating forces.
Reynolds Model law is applicable for pipe flows and submarines airplanes, fully submerged bodies etc.
For dynamic similarity the Reynolds number must be the same.
Reynolds Number Re = VD/v
where V is the velocity, D is the pipe diameter, ν is the kinematic viscosity
Calculation:
Given:
ν1= 0.01 stoke, V1 = 2 m/s, D1 = D2 = 15 cm, ν2 = 0.03 stoke,
Now For dynamic similarity, Reynold’s number would be the same.
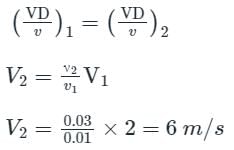
For Dynamic similarity the ratio of corresponding forces acting at the corresponding points should be the same in the model and prototype, the ratio of these forces are called dimensionless numbers.
Therefore for the dynamic similarity between the model and prototype the dimensionless should also be the same. The models are designed on the basis of dominating forces.
Reynolds Model law is applicable for pipe flows and submarines airplanes, fully submerged bodies etc.
For dynamic similarity the Reynolds number must be the same.
Reynolds Number Re = VD/v
where V is the velocity, D is the pipe diameter, ν is the kinematic viscosity
Calculation:
Given:
ν1= 0.01 stoke, V1 = 2 m/s, D1 = D2 = 15 cm, ν2 = 0.03 stoke,
Now For dynamic similarity, Reynold’s number would be the same.
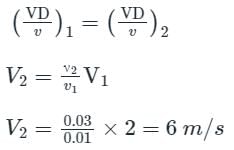

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Water having kinematic viscosity of 0.01 stoke flows at a velocity of 2 m/s in a pipe of 15 cm diameter. For dynamic similarity, the velocity of oil of kinematic viscosity of 0.03 stoke in a pipe of same diameter will bea)0.33 m/sb)0.66 m/sc)2 m/sd)6 m/sCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























