JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in phot...
Start Learning for Free
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves
- a)8 molecules of ATP
- b)6 molecules of ATP
- c)18 molecules of ATP
- d)10 molecules of ATP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 mo...
Synthesis of glucose molecule in photosynthesis involves following reaction:
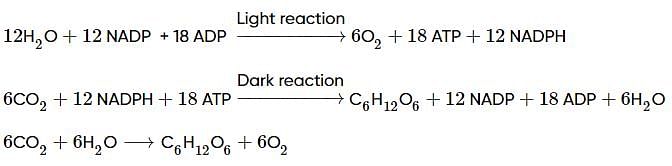
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 mo...
The Synthesis of Glucose in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process that green plants use to manufacture carbohydrates, such as glucose, from carbon dioxide and water, using energy from sunlight. The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
The synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves several steps, including the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is used to generate ATP and NADPH, which are required for the light-independent reactions.
The Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. The pigments, such as chlorophyll, absorb light energy, which is used to generate ATP and NADPH. The light-dependent reactions can be summarized as follows:
1. Absorption of Light Energy by Pigments
The pigments in the thylakoid membranes absorb light energy, which excites electrons and generates ATP and NADPH.
2. Splitting of Water Molecules
Water molecules are split by the energy from sunlight, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. The oxygen gas is released into the atmosphere, while the hydrogen ions are used in the light-independent reactions.
3. Generation of ATP and NADPH
The energy from sunlight is used to generate ATP and NADPH. The ATP and NADPH are used in the light-independent reactions to synthesize glucose.
The Light-Independent Reactions
The light-independent reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts. The carbon dioxide molecules are fixed into carbohydrates, such as glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions can be summarized as follows:
1. Fixation of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide molecules are fixed by the enzyme Rubisco, which catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
2. Synthesis of Carbohydrates
The fixed carbon dioxide molecules are used to synthesize carbohydrates, such as glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
3. Regeneration of RuBP
The remaining carbon molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, which is used again in the fixation of carbon dioxide.
The Energy Requirement
The synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves the consumption of 18 molecules of ATP and 12 molecules of NADPH. The ATP and NADPH are generated by the light-dependent reactions, which require light energy and the splitting of water molecules. Therefore, photosynthesis is an energy-intensive process that requires sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis is the process that green plants use to manufacture carbohydrates, such as glucose, from carbon dioxide and water, using energy from sunlight. The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
The synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves several steps, including the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is used to generate ATP and NADPH, which are required for the light-independent reactions.
The Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. The pigments, such as chlorophyll, absorb light energy, which is used to generate ATP and NADPH. The light-dependent reactions can be summarized as follows:
1. Absorption of Light Energy by Pigments
The pigments in the thylakoid membranes absorb light energy, which excites electrons and generates ATP and NADPH.
2. Splitting of Water Molecules
Water molecules are split by the energy from sunlight, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. The oxygen gas is released into the atmosphere, while the hydrogen ions are used in the light-independent reactions.
3. Generation of ATP and NADPH
The energy from sunlight is used to generate ATP and NADPH. The ATP and NADPH are used in the light-independent reactions to synthesize glucose.
The Light-Independent Reactions
The light-independent reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts. The carbon dioxide molecules are fixed into carbohydrates, such as glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions can be summarized as follows:
1. Fixation of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide molecules are fixed by the enzyme Rubisco, which catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
2. Synthesis of Carbohydrates
The fixed carbon dioxide molecules are used to synthesize carbohydrates, such as glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
3. Regeneration of RuBP
The remaining carbon molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, which is used again in the fixation of carbon dioxide.
The Energy Requirement
The synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves the consumption of 18 molecules of ATP and 12 molecules of NADPH. The ATP and NADPH are generated by the light-dependent reactions, which require light energy and the splitting of water molecules. Therefore, photosynthesis is an energy-intensive process that requires sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involvesa)8 molecules of ATPb)6 molecules of ATPc)18 molecules of ATPd)10 molecules of ATPCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.