Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > What is e coli bacteria and explain its struc...
Start Learning for Free
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?
E. coli, (Escherichia coli), species of bacterium that normally inhabits the stomach and intestines. When E. coli is consumed in contaminated water, milk, or food or is transmitted through the bite of a fly or other insect, it can cause gastrointestinal illness. Mutations can lead to strains that cause diarrhea by giving off toxins, invading the intestinal lining, or sticking to the intestinal wall. Therapy for gastrointestinal illness consists largely of fluid replacement, though specific drugs are effective in some cases. The illness is usually self-limiting, with no evidence of long-lasting effects. However, dangerous strains, such as E. coli O157: H7 and E. coli O104:H4, can cause bloody diarrhea, kidney failure, and death in extreme cases. Proper cooking of meat and washing of produce can prevent infection from contaminated food sources. E. coli also can cause urinary tract infections in women.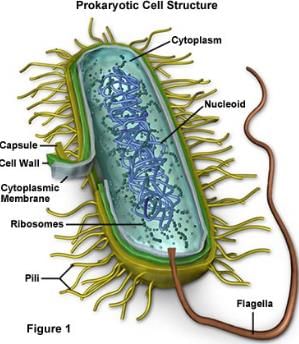

Community Answer
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?
E. coli Bacteria: Structure and Functions
E. coli, short for Escherichia coli, is a type of bacteria commonly found in the lower intestines of warm-blooded organisms, including humans. While most strains of E. coli are harmless and even beneficial, some can cause illnesses, ranging from mild gastrointestinal issues to severe infections. Understanding the structure of E. coli is crucial in comprehending its functions and pathogenicity.
1. Morphology:
E. coli bacteria are Gram-negative, rod-shaped organisms with a typical length of 2-6 μm and a diameter of approximately 0.5-1 μm. These bacteria have a single, circular chromosome containing their genetic material, which is encased within the cell membrane.
2. Outer Membrane:
The outer membrane of E. coli is composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), proteins, and phospholipids. It acts as a protective barrier against harmful substances, including certain antibiotics. The outer membrane also contains porins, which allow the passage of small molecules and ions.
3. Cell Wall:
The cell wall of E. coli is comprised of peptidoglycan, a mesh-like structure composed of sugar molecules and amino acid chains. This layer provides structural support and protection to the bacterium. In addition, the cell wall is responsible for maintaining the shape of the cell.
4. Cell Membrane:
The cell membrane, also known as the inner membrane, lies beneath the outer membrane and plays a crucial role in regulating the transport of molecules into and out of the cell. It contains various proteins, such as transporters and enzymes, which facilitate important cellular processes.
5. Flagella:
E. coli bacteria possess long, whip-like appendages called flagella, which enable them to move towards favorable environments or away from harmful substances. These flagella are composed of a protein called flagellin and rotate like propellers, propelling the bacterium through its liquid environment.
6. Pili:
Pili, also known as fimbriae, are hair-like projections found on the surface of E. coli bacteria. They play a crucial role in attachment to host cells and the formation of biofilms. Pili contain proteins that allow the bacterium to adhere to specific receptors on host tissues, facilitating colonization and infection.
7. Plasmids:
E. coli bacteria can contain small, circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which exist alongside the main chromosome. Plasmids often carry genes that provide the bacterium with advantages, such as antibiotic resistance or the ability to produce toxins. These plasmids can be transferred between bacteria through a process called conjugation.
Conclusion:
Understanding the structure of E. coli bacteria provides insights into its functions and pathogenicity. Its various components, such as the outer membrane, cell wall, cell membrane, flagella, pili, and plasmids, contribute to the bacterium's ability to survive, move, adhere to host tissues, and cause infections. By studying the structure and functions of E. coli, scientists can develop strategies to prevent and treat E. coli-related illnesses.
E. coli, short for Escherichia coli, is a type of bacteria commonly found in the lower intestines of warm-blooded organisms, including humans. While most strains of E. coli are harmless and even beneficial, some can cause illnesses, ranging from mild gastrointestinal issues to severe infections. Understanding the structure of E. coli is crucial in comprehending its functions and pathogenicity.
1. Morphology:
E. coli bacteria are Gram-negative, rod-shaped organisms with a typical length of 2-6 μm and a diameter of approximately 0.5-1 μm. These bacteria have a single, circular chromosome containing their genetic material, which is encased within the cell membrane.
2. Outer Membrane:
The outer membrane of E. coli is composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), proteins, and phospholipids. It acts as a protective barrier against harmful substances, including certain antibiotics. The outer membrane also contains porins, which allow the passage of small molecules and ions.
3. Cell Wall:
The cell wall of E. coli is comprised of peptidoglycan, a mesh-like structure composed of sugar molecules and amino acid chains. This layer provides structural support and protection to the bacterium. In addition, the cell wall is responsible for maintaining the shape of the cell.
4. Cell Membrane:
The cell membrane, also known as the inner membrane, lies beneath the outer membrane and plays a crucial role in regulating the transport of molecules into and out of the cell. It contains various proteins, such as transporters and enzymes, which facilitate important cellular processes.
5. Flagella:
E. coli bacteria possess long, whip-like appendages called flagella, which enable them to move towards favorable environments or away from harmful substances. These flagella are composed of a protein called flagellin and rotate like propellers, propelling the bacterium through its liquid environment.
6. Pili:
Pili, also known as fimbriae, are hair-like projections found on the surface of E. coli bacteria. They play a crucial role in attachment to host cells and the formation of biofilms. Pili contain proteins that allow the bacterium to adhere to specific receptors on host tissues, facilitating colonization and infection.
7. Plasmids:
E. coli bacteria can contain small, circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which exist alongside the main chromosome. Plasmids often carry genes that provide the bacterium with advantages, such as antibiotic resistance or the ability to produce toxins. These plasmids can be transferred between bacteria through a process called conjugation.
Conclusion:
Understanding the structure of E. coli bacteria provides insights into its functions and pathogenicity. Its various components, such as the outer membrane, cell wall, cell membrane, flagella, pili, and plasmids, contribute to the bacterium's ability to survive, move, adhere to host tissues, and cause infections. By studying the structure and functions of E. coli, scientists can develop strategies to prevent and treat E. coli-related illnesses.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?
Question Description
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?.
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?.
Solutions for What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure?, a detailed solution for What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? has been provided alongside types of What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is e coli bacteria and explain its structure? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























