Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > What is the difference between himalayan rive...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ...
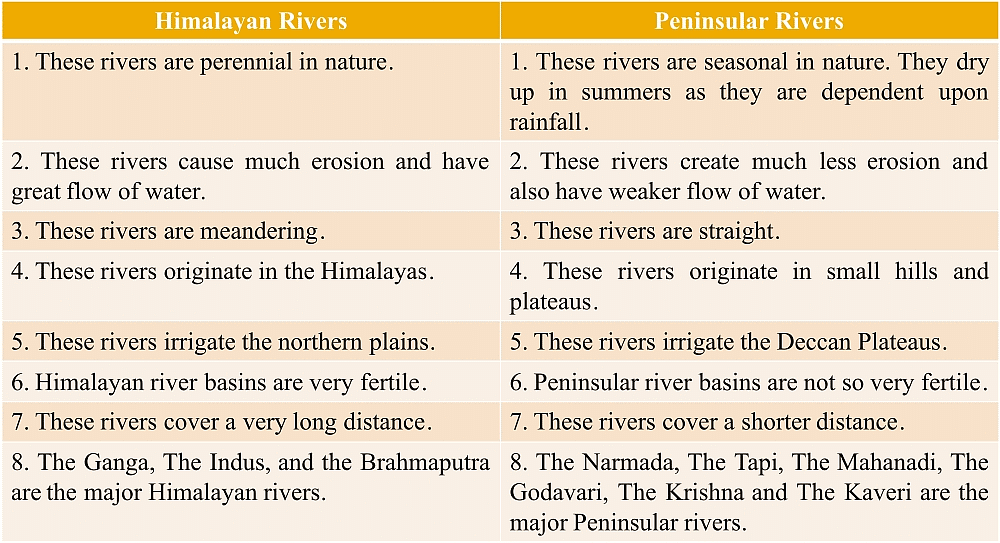
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ...
Himalayan Rivers
Himalayan rivers are the rivers that originate from the Himalayan mountain range, which stretches across several countries including India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China. These rivers are characterized by their large volume of water, swift flow, and high erosive power. Here are some key differences between Himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers:
1. Origin and Course
- Himalayan rivers originate from the glaciers and snowfields of the Himalayas. They flow in a southward or southeast direction and traverse through the mountainous regions, cutting deep gorges and valleys.
- Peninsular rivers, on the other hand, originate from the plateau region of the Indian peninsula. They flow towards the east and drain into the Bay of Bengal or the Arabian Sea. These rivers have relatively gentle slopes and flow through the plains.
2. Volume of Water
- Himalayan rivers receive a significant amount of water from melting glaciers and heavy rainfall in the mountainous regions. As a result, they have a high volume of water throughout the year. For example, the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers carry a massive amount of water, especially during the monsoon season.
- Peninsular rivers, in comparison, have a relatively lower volume of water. They depend on seasonal rainfall for their water supply, and their flow fluctuates significantly throughout the year.
3. Gradient and Flow
- Himalayan rivers have a steep gradient due to the rugged terrain they traverse. This leads to a swift flow and high erosive power, resulting in the formation of deep valleys, gorges, and alluvial plains in the foothills. The force of these rivers is harnessed to generate hydroelectric power.
- Peninsular rivers have a gentle gradient as they flow through the plains. They have a slower flow and lower erosive power, leading to the formation of broad river valleys and deltas. The slower flow makes them suitable for irrigation purposes.
4. Deposition and Sediment Load
- Himalayan rivers carry a significant amount of sediments due to their high erosive power. These sediments are deposited along their course, leading to the formation of fertile alluvial plains. The deposition of sediments also contributes to the formation of river islands and distributaries.
- Peninsular rivers carry a lesser amount of sediments due to their lower erosive power. As a result, their deposition is limited, and they do not have extensive alluvial plains like the Himalayan rivers. However, they still contribute to the formation of deltas at their mouths.
In conclusion, the key differences between Himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers lie in their origin, course, volume of water, gradient, flow, and deposition patterns. While Himalayan rivers are characterized by their large volume, swift flow, and high erosive power, peninsular rivers have a relatively lower volume, slower flow, and gentler gradients. Understanding these differences helps in comprehending the diverse characteristics and significance of these river systems in the Indian subcontinent.
Himalayan rivers are the rivers that originate from the Himalayan mountain range, which stretches across several countries including India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China. These rivers are characterized by their large volume of water, swift flow, and high erosive power. Here are some key differences between Himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers:
1. Origin and Course
- Himalayan rivers originate from the glaciers and snowfields of the Himalayas. They flow in a southward or southeast direction and traverse through the mountainous regions, cutting deep gorges and valleys.
- Peninsular rivers, on the other hand, originate from the plateau region of the Indian peninsula. They flow towards the east and drain into the Bay of Bengal or the Arabian Sea. These rivers have relatively gentle slopes and flow through the plains.
2. Volume of Water
- Himalayan rivers receive a significant amount of water from melting glaciers and heavy rainfall in the mountainous regions. As a result, they have a high volume of water throughout the year. For example, the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers carry a massive amount of water, especially during the monsoon season.
- Peninsular rivers, in comparison, have a relatively lower volume of water. They depend on seasonal rainfall for their water supply, and their flow fluctuates significantly throughout the year.
3. Gradient and Flow
- Himalayan rivers have a steep gradient due to the rugged terrain they traverse. This leads to a swift flow and high erosive power, resulting in the formation of deep valleys, gorges, and alluvial plains in the foothills. The force of these rivers is harnessed to generate hydroelectric power.
- Peninsular rivers have a gentle gradient as they flow through the plains. They have a slower flow and lower erosive power, leading to the formation of broad river valleys and deltas. The slower flow makes them suitable for irrigation purposes.
4. Deposition and Sediment Load
- Himalayan rivers carry a significant amount of sediments due to their high erosive power. These sediments are deposited along their course, leading to the formation of fertile alluvial plains. The deposition of sediments also contributes to the formation of river islands and distributaries.
- Peninsular rivers carry a lesser amount of sediments due to their lower erosive power. As a result, their deposition is limited, and they do not have extensive alluvial plains like the Himalayan rivers. However, they still contribute to the formation of deltas at their mouths.
In conclusion, the key differences between Himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers lie in their origin, course, volume of water, gradient, flow, and deposition patterns. While Himalayan rivers are characterized by their large volume, swift flow, and high erosive power, peninsular rivers have a relatively lower volume, slower flow, and gentler gradients. Understanding these differences helps in comprehending the diverse characteristics and significance of these river systems in the Indian subcontinent.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points?
Question Description
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points?.
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points?.
Solutions for What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between himalayan rivers and peninsular rivers ? write at least 4-5 points? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Test: The Fundamental Unit of Life- Case Based Type Questions- 1
Test | 10 questions
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























