Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)...
Start Learning for Free
A column with maximum equivalent length has
- a)both ends hinged
- b)long columns
- c)one end fixed and the other end hinged
- d)one end fixed and the other end free
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long co...
**Column with Maximum Equivalent Length**
The correct answer to the question is option 'd' - one end fixed and the other end free. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
**Introduction to Columns**
In structural engineering, a column is a vertical structural member designed to support compressive loads. Columns are critical elements in many structures, such as buildings, bridges, and towers. They are subjected to axial compressive forces that act along their length.
**Column Buckling**
When a column is subjected to a compressive load, it tends to buckle or deform laterally. Buckling occurs when the applied load exceeds the critical buckling load, causing the column to bend and lose its stability. Buckling can result in catastrophic failure of the column and the entire structure.
**Effective Length Factor**
The effective length factor (K) is used to determine the buckling behavior of a column. It takes into account the boundary conditions at the ends of the column and affects the critical buckling load. The value of K depends on the support conditions at the column ends.
**Different Support Conditions**
Let's consider the different support conditions for column ends:
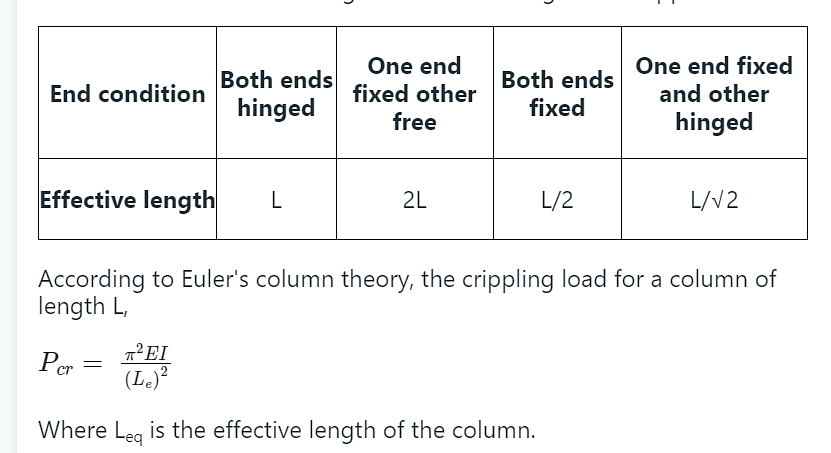
1. Both Ends Hinged (Pinned): In this case, both ends of the column are free to rotate, allowing the column to buckle easily. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 1.0.
2. Both Ends Fixed: When both ends of the column are fixed, they are restrained against rotation. This significantly increases the column's resistance to buckling. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 0.5.
3. One End Fixed and the Other End Hinged: This condition provides partial restraint to the column against rotation. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 0.7.
4. One End Fixed and the Other End Free: This condition provides partial restraint at one end and allows rotation at the other end. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 2.0.
**Explanation of the Answer**
The maximum equivalent length occurs when one end of the column is fixed and the other end is free. In this condition, the effective length factor (K) is 2.0, which is greater than any other support condition. A higher effective length factor leads to a lower critical buckling load, making the column more susceptible to buckling.
In practical terms, a column with one end fixed and the other end free has the highest risk of buckling and requires additional design considerations to ensure its stability. The fixed end provides some resistance against buckling, while the free end allows for lateral deformations.
Therefore, option 'd' - one end fixed and the other end free - is the correct answer as it represents the column with the maximum equivalent length.
The correct answer to the question is option 'd' - one end fixed and the other end free. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
**Introduction to Columns**
In structural engineering, a column is a vertical structural member designed to support compressive loads. Columns are critical elements in many structures, such as buildings, bridges, and towers. They are subjected to axial compressive forces that act along their length.
**Column Buckling**
When a column is subjected to a compressive load, it tends to buckle or deform laterally. Buckling occurs when the applied load exceeds the critical buckling load, causing the column to bend and lose its stability. Buckling can result in catastrophic failure of the column and the entire structure.
**Effective Length Factor**
The effective length factor (K) is used to determine the buckling behavior of a column. It takes into account the boundary conditions at the ends of the column and affects the critical buckling load. The value of K depends on the support conditions at the column ends.
**Different Support Conditions**
Let's consider the different support conditions for column ends:
1. Both Ends Hinged (Pinned): In this case, both ends of the column are free to rotate, allowing the column to buckle easily. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 1.0.
2. Both Ends Fixed: When both ends of the column are fixed, they are restrained against rotation. This significantly increases the column's resistance to buckling. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 0.5.
3. One End Fixed and the Other End Hinged: This condition provides partial restraint to the column against rotation. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 0.7.
4. One End Fixed and the Other End Free: This condition provides partial restraint at one end and allows rotation at the other end. The effective length factor for this condition is K = 2.0.
**Explanation of the Answer**
The maximum equivalent length occurs when one end of the column is fixed and the other end is free. In this condition, the effective length factor (K) is 2.0, which is greater than any other support condition. A higher effective length factor leads to a lower critical buckling load, making the column more susceptible to buckling.
In practical terms, a column with one end fixed and the other end free has the highest risk of buckling and requires additional design considerations to ensure its stability. The fixed end provides some resistance against buckling, while the free end allows for lateral deformations.
Therefore, option 'd' - one end fixed and the other end free - is the correct answer as it represents the column with the maximum equivalent length.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long co...
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A column with maximum equivalent length hasa)both ends hingedb)long columnsc)one end fixed and the other end hingedd)one end fixed and the other end freeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























