ACT Exam > ACT Questions > The rate of a reversible chemical reaction de...
Start Learning for Free
The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.
In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.
In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:
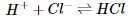
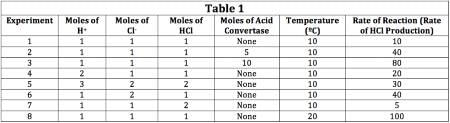
The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.
Q. What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?
- a)Seconds/Mole
- b)Moles/Moles
- c)Moles/Second
- d)Moles/Liter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, in...
The passage describes that the reaction rate can be found by dividing the amount of chemicals produced in a reaction (moles) by the time it takes to produce them (seconds/minutes/hours/etc). The only answer choice that fits this pattern is moles/second. The other answer choices do contain the amount of chemicals produced but do not contain the time it takes to produce them.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Question Description
The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The rate of a reversible chemical reaction depends on many factors, including concentrations of the reactants and products, temperature, and presence of enzymes called catalysts. In the forward reaction, two reactants combine to form one product. However, in a reverse reaction, the product is broken down into the two reactants.In order for a forward reaction to occur, the reactants moving around in the test tube must physically interact with each other. The more often reactants interact with each other, the more produce is formed in the same amount of time. The speed at which reactants combine into products (the rate of the reaction) can be calculated by dividing the amount of a chemical produced in a reaction (often measured in moles) by the time it takes to produce that amount.In order to determine the effects of reactant and product concentration, temperature, and presence of catalysts on the rate of a reaction, a scientist studied the following reaction:The scientist varied the conditions of the experiment and measured the rate of the reaction. The results are outlined in Table 1. The units of concentration are moles per liter.Q.What is a possible unit of a rate of reaction?a)Seconds/Moleb)Moles/Molesc)Moles/Secondd)Moles/LiterCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















