ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Sound waves travel through a medium by mechan...
Start Learning for Free
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so.
Study 1
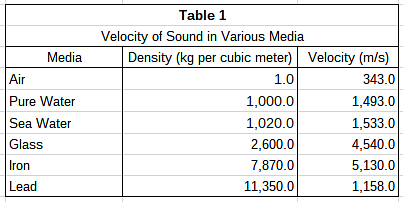
A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.
A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.
Study 2
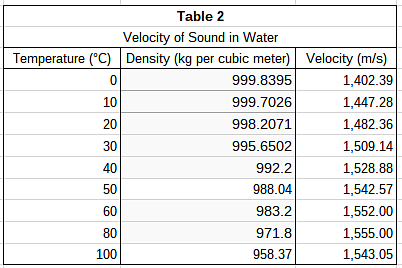
The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.
The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.
According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?
- a)It either increases or decreases.
- b)It does not change.
- c)It decreases.
- d)It increases.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the par...
The velocity of sound in different media is listed in the third column of Table 1. Density of the media increases as you move down the column. Velocity increases along with density except between iron and lead. This means that no direct relationship between density and velocity can be drawn; the velocity of sound can either increase or decrease as density increases.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Sound waves travel through a medium by mechanically disturbing the particles of that medium. As particles in the medium are displaced by the sound wave, they in turn act upon neighboring particles. In this fashion, the wave travels through the medium through a parallel series of disturbed particles. Like in other forms of motion, the rate at which the sound wave travels can be measured by dividing the distance over which the wave travels by the time required for it to do so. Study 1A group of students hypothesizes that the velocity of sound is dependent upon the density of the medium through which it passes. They propose that with more matter in a given space, each particle needs to travel a shorter distance to disturb the adjacent particles. Using two microphones and a high speed recording device, the students measured the delay from the first microphone to the second. They chose a variety of media, shown in Table 1, and measured the velocity of sound through each using their two-microphone setup. The results are found in Table 1.Study 2The students wanted to test their hypothesis by using the same medium at different densities. To do this, they heated pure water to various temperatures and repeated the procedure described in Study 1. Their results can be found in Table 2.According to the data in Study 1, as density increases, what happens to the velocity of sound?a)It either increases or decreases.b)It does not change.c)It decreases.d)It increases.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























