ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
The peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.
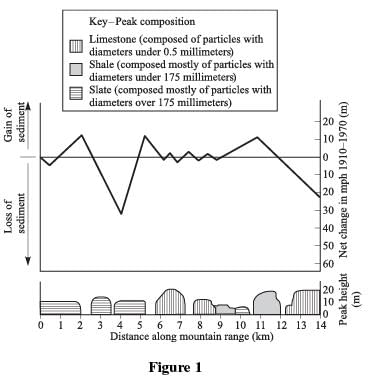
Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.
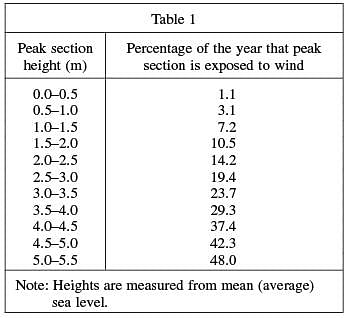
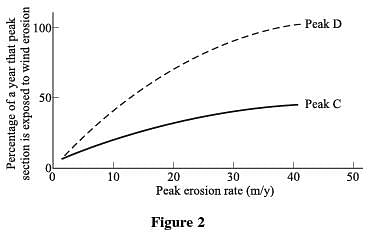
Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.
The peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.

Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.

Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.

Q. According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:
- a)heights of the two peaks.
- b)force of the winds on the two peaks.
- c)composition of the two peaks.
- d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
Figure 2 shows that Peak D is exposed to wind erosion for a greater percentage of the year than Peak C. Table 1 suggests that the percentage of the peak exposed to wind is directly proportional to peak section height.
Therefore, because Peak D is exposed to the wind for longer than Peak C is, Peak D must be taller than Peak C. This information best supports answer choice A.
Therefore, because Peak D is exposed to the wind for longer than Peak C is, Peak D must be taller than Peak C. This information best supports answer choice A.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageThe peaks of mountains often lose sediment due to wind erosion. Figure 1 shows mountain peak compositions, mountain heights, in meters (m), and the net change in meters (m), in mean peak height (MPH) from 1910 to 1970 along a section of the Rocky Mountains. A net negative change in MPH indicates a net loss of sediment and a net positive change in MPH indicates a gain of sediment.Table 1 shows the percentage of a year that horizontal sections of a mountain are exposed to wind.Figure 2 shows Peak C and D erosion rates, in m/y, as they relate to percentage of a year that mountain peak section is exposed to wind.Q.According to Figures 1 and 2, the difference between Peak C and Peak D erosion rates could best be explained as a difference in the:a)heights of the two peaks.b)force of the winds on the two peaks.c)composition of the two peaks.d)annual snowfall on the two peaks.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























