SAT Exam > SAT Questions > Question refer to the following information.I...
Start Learning for Free
Question refer to the following information.
If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .
This relationship is known as Little’s law.
The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.
If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .
This relationship is known as Little’s law.
The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.
Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)
Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store ...
The correct answer is 60.
The estimated average number of shoppers in the original store at any time is 45.
In the new store, the manager estimates that an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store, which is equivalent to 1.5 shoppers per minute.
The manager also estimates that each shopper stays in the store for an average of 12 minutes.
Thus, by Little’s law, there are, on average, N = rt = (1.5)(12) = 18 shoppers in the new store at any time.
This is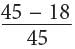 × 100 = 60 percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time.
× 100 = 60 percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time.
The estimated average number of shoppers in the original store at any time is 45.
In the new store, the manager estimates that an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store, which is equivalent to 1.5 shoppers per minute.
The manager also estimates that each shopper stays in the store for an average of 12 minutes.
Thus, by Little’s law, there are, on average, N = rt = (1.5)(12) = 18 shoppers in the new store at any time.
This is
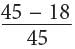 × 100 = 60 percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time.
× 100 = 60 percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time.

|
Explore Courses for SAT exam
|

|
Similar SAT Doubts
Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? for SAT 2025 is part of SAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SAT exam syllabus. Information about Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?.
Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? for SAT 2025 is part of SAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SAT exam syllabus. Information about Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Question refer to the following information.If shoppers enter a store at an average rate of r shoppers per minute and each stays in the store for an average time of T minutes, the average number of shoppers in the store, N, at any one time is given by the formula N = rT .This relationship is known as Little’s law.The owner of the Good Deals Store estimates that during business hours, an average of 3 shoppers per minute enter the store and that each of them stays an average of 15 minutes. The store owner uses Little’s law to estimate that there are 45 shoppers in the store at any time.Q. The owner of the Good Deals Store opens a new store across town. For the new store, the owner estimates that, during business hours, an average of 90 shoppers per hour enter the store and each of them stays an average of 12 minutes. The average number of shoppers in the new store at any time is what percent less than the average number of shoppers in the original store at any time? (Note: Ignore the percent symbol when entering your answer. For example, if the answer is 42.1%, enter 42.1)Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for SAT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























