ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
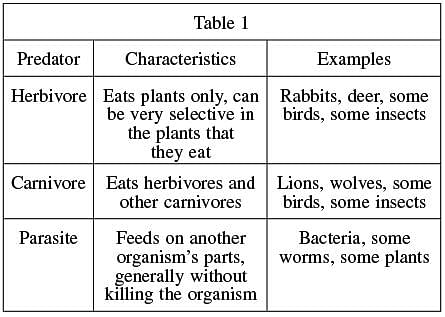
Predation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.
Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.
Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.
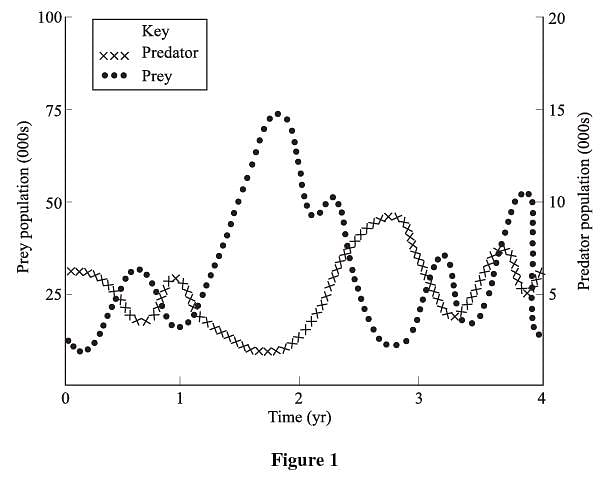
Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.
Passage
Predation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.

Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.
Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.
Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.

Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:
- a)a predator only.
- b)both a parasite and a predator.
- c)prey only.
- d)both a predator and prey.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
The best answer is d. Table 1 lists characteristics of certain predators. Since “herbivore” is listed in the table, a herbivore is a predator. The passage also indicates that some scientists contend that herbivores are predators. According to Table 1, carnivores eat herbivores, which means that a herbivore is also a prey animal.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassagePredation is an interaction between individuals of 2 species in which one is harmed (the prey), and the other is helped (the predator). Predation can occur among plants and animals as well as between plants and animals. Some biologists contend that herbivores, or plant eaters, are predators. Table 1 indicates some characteristics and examples of certain predators.Predation is very important in maintaining a natural balance in any given ecosystem. For example, without predators, prey populations tend to grow exponentially.Without prey, predator populations tend to decline exponentially. Predators consume individual members of the prey population, thereby controlling the overall numbers in the ecosystem. The number of prey consumed depends on the number of prey present as well as the number of predators present. The rate of change in the number of prey is a function of the birth of new prey minus the death of other prey, due either to predation or other causes. The death rate is assumed to depend on the number of prey available and the number of predators. The rate of change in the number of predators is a function of the births of new predators—which depends on the number of prey—minus the death of some predators.Over long periods of time, predator and prey tend to balance each other out. This is called the predator-prey cycle. Prey numbers will increase when predator numbers decrease. When the number of prey reaches a certain point, predators will start to increase until they eat enough prey to cause a decline in prey numbers. When this happens, the number of predators will begin to decrease because they can’t find enough prey to eat, and the cycle will begin again. Figure 1 represents an example of a predator-prey cycle.Q. Based on information in the passage and in Table 1, an herbivore is:a)a predator only.b)both a parasite and a predator.c)prey only.d)both a predator and prey.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























