ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Amino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water (a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.
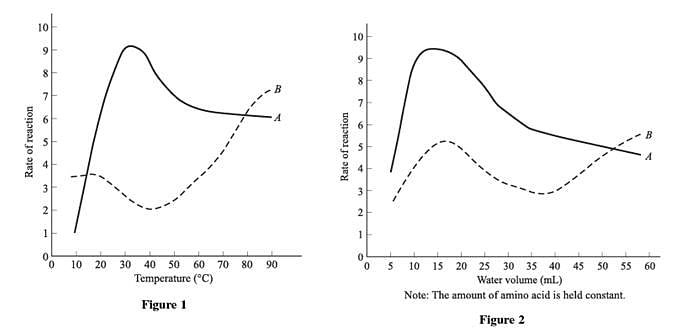
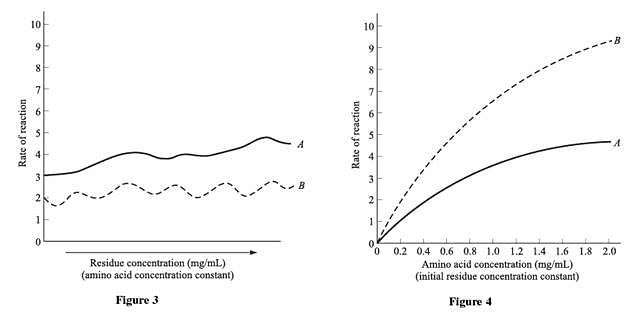
Amino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water (a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.


Q. A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?
- a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.
- b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.
- c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.
- d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
Figure 3 shows that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is not dependent on the residue concentration. Figure 4 shows that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on the amino acid concentration. Therefore, the figures do not support the researcher’s claims that the reaction of Amino Acid B is dependent on both concentrations.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAmino acids are considered the building blocks of protein in the body. Amino acids combine with each other to form chains called peptides, which then combine to form proteins. The human body requires twenty different amino acids, whose combinations produce every essential protein in the body. When amino acids form peptides, the residue is what is left after the amino acid sheds a molecule of water(a hydrogen ion from one end and a hydroxide ion from the other end). The reaction rate is the factor by which the protein is able to build itself up through the combination of peptides. Figures 1–3 show the effects that changes in temperature, water volume, and residue concentration have on the rate of reaction of residue when Amino Acids A and B are present. Figure 4 shows the effects that changes in the concentrations of Amino Acids A and B have on the rates of reaction in residue solutions of the same concentration.Q.A researcher claims that the reaction rate of Amino Acid B is dependent on both residue concentration and amino acid concentration. Do the data in Figures 3 and 4 support this claim?a)No, the reaction rate is dependent on the amino acid concentration, but not on the residue concentration.b)No, the reaction rate is not dependent on either the residue concentration or the amino acid concentration.c)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on both the residue concentration and the amino acid concentration.d)Yes, the reaction rate is dependent on the residue concentration, but not on the amino acid concentration.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























