ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Asian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.
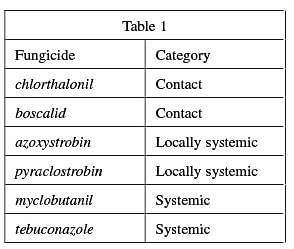
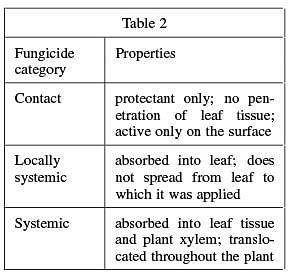
Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.
ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.
The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.
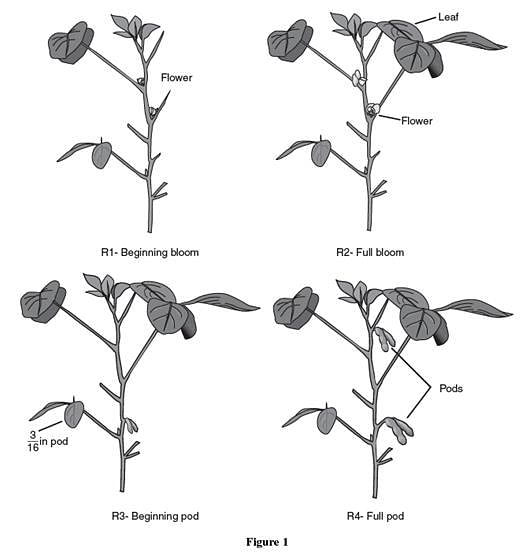
Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).
Passage
Asian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.
Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.


ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.
The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.
Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).

Q. Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?
- a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.
- b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.
- c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.
- d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
According to Table 2, systemic fungicides are most effective because they are absorbed into the leaf tissue and translocated throughout the plant. Table 1 indicates that myclobutanil is a systemic fungicide. Because the question asks you to put the fungicides in order of increasing effectiveness, myclobutanil should be last on the list. Eliminate answer choices A and D. The data indicate that contact fungicides are the least effective and that boscalid is a contact fungicide. Therefore, boscalid should be first on the list.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageAsian soybean rust (ASR) is a disease caused by the fungus Phakospora pachyrhizi. ASR spreads by windborne spores that infect soybean leaves. As rust lesions mature, they produce thousands of additional spores. Over time, large spore loads build up within fields and across large geographical areas. In 2004, this disease was detected in nine states in the American southwest, and by 2005 it had invaded several other states. ASR can drastically reduce crop yields in areas where it commonly occurs, so monitoring and application of preventive measures such as fungicide will likely be necessary.Certain fungicides have been tested for their effectiveness against ASR. These fungicides are listed in Table 1. The simplest classification of fungicides divides them into three categories: contact, locally systemic, and systemic. Properties of these fungicide categories are given in Table 2.ASR infections generally begin in the lower leaf canopy where humidity is higher and leaves stay wet for longer periods. For this reason, the lower soybean leaf canopy is the primary spray target. Both upper and lower leaf surfaces must be sprayed. Coverage as dense as 400 spray droplets per square inch is considered ideal.The different properties of fungicide types have important implications for spray application. Contact and locally systemic fungicides require better spray coverage than systemic fungicides. Contact fungicides, because they do not penetrate the plant tissue, are more easily washed off the leaf by rain. This results in a shorter residual control period and more frequent re-application of the fungicide.Tests have shown that fungicides effectiveness varies based on the soybean growth stage at which the fungicide is applied. Figure 1 identifies some of the different stages of soybean growth. Soybean leaves can be infected at any time with ASR. However, research has shown that the most critical time to protect soybean plants with fungicides is from the R1 through R5 growth stages. Fungicide applications should not be initiated after the R5 growth stage (seed development and mature plant).Q.Equal amounts of azoxystrobin, boscalid, and myclobutanil were applied to three different soybean plants during Growth Stage 3. After 24-hours, each of the plants was sprayed with water. Based on the data, which of the following represents the order, from least effective to most effective, of the fungicides’ likelihood of preventing ASR?a)myclobutanil, azoxystrobin, boscalid.b)azoxystrobin, boscalid, myclobutanil.c)boscalid, azoxystrobin, myclobutanil.d)myclobutanil, boscalid, azoxystrobin.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























