ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Turf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.
A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.
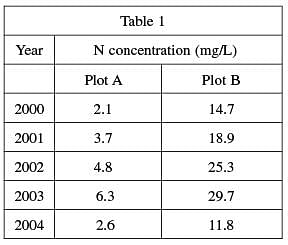
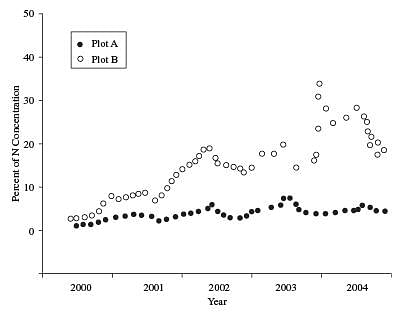
Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.
Passage
Turf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.
A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.
Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.


Q. In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?
- a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.
- b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.
- c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.
- d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
According to the passage, the nitrogen levels in the fertilizer applied to Plot B were reduced in 2004. However, Table 1 shows that the nitrogen concentration in the leachate from Plot B was 11.8 mg/L, which is still considered unsafe. In 2005, the concentration had gone down to a safe 8.2 mg/L. Therefore, you can conclude that it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in the leachate. The other answer choices are not supported by the data.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageTurf grasses are used throughout the United States in many suburban lawns. Kentucky bluegrass is the most common type of turf grass used in the northern part of the United States. To keep lawns green and healthy, many homeowners apply fertilizer up to five times a year. Inorganic fertilizers are becoming more popular, and contain three common elements – nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium – for the development of plant color, strength, and health. Most turf grass lawns do not use all of the nutrients provided in the fertilizer, which means that much of the nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium remains in the soil. When water enters the soil, it accumulates a portion of the excess nitrogen from the soil. This water, now termed leachate, flows into surrounding waterways. The leaching of high concentrations of nitrogen into natural waterways can throw off the environmental equilibrium of the aquatic ecosystem, often resulting in an increase in plant growth that can have a negative impact on the native fish populations.A study was performed to examine the degree of nitrogen leaching in Kentucky bluegrass turf; 2 one-acre plots of turf were compared. The scientists conducting the study relied completely on natural rainwater to irrigate the test plots. Each plot received fertilizer applications containing different levels of nitrogen two times per week during the months of April and September for 5 years. The plots had a 5% slope to facilitate leaching; leachate was collected in one-liter jugs. The leachate collected from each plot was measured for nitrogen concentration.Plot A, received a low nitrogen application, 98 kilograms of N per acre from 2000 to 2004. Plot B, received an initially high nitrogen application, 245 kilograms of N per acre from 2000–2002. In the last year of the study, the amount of nitrogen in the fertilizer was decreased to 196 kilograms of N per acre for Plot B. Table 1 shows the average nitrogen concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) in the leachate collected from each plot during each year. Figure 1 shows the percent concentration of nitrogen in the leachate.Q.In 2005, it was found that average nitrogen levels in the leachate from Plot B were 8.2 mg/L. The data from the study supports which of the following conclusions?a)Kentucky bluegrass should not be used for lawns in suburbs near a public waterway.b)Once high-nitrogen fertilizer has been applied to a suburban lawn, nitrogen levels in the leachate will remain high, even if low-nitrogen fertilizer is later applied.c)Following the application of low-nitrogen fertilizers, it will take more than one year to reach safe nitrogen levels in leachate from suburban lawns previously fertilized with high-nitrogen fertilizer.d)The measurable concentration of nitrogen in leachate from suburban lawns will always be within the range considered safe by the Environmental Protection Agency, as long as irrigation is kept to a minimum.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























