Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame AB...
Start Learning for Free
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy is
- a)3
- b)2
- c)6
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fi...
Problem Analysis
We are given a single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD with fixed column ends. We need to determine the kinematic indeterminacy of the frame.
Solution
The kinematic indeterminacy of a structure refers to the number of redundant members or joints that can be removed without causing any change in the stability or equilibrium of the structure.
In the given portal frame, the column ends are fixed, which means they are fully restrained against rotation and translation. This implies that there is no relative rotation or displacement between the column ends and the foundation.
Analysis of the Frame
To determine the kinematic indeterminacy, we need to analyze the frame and identify the degrees of freedom.
1. Number of Joints (J): In the given frame, there are four joints: A, B, C, and D.
2. Number of Members (M): There are three members: AB, BC, and CD.
Degree of Freedom Analysis
Next, we analyze the degrees of freedom at each joint to determine the kinematic indeterminacy.
1. Joint A:
- Vertical Displacement (V): Since the column end is fixed, there is no vertical displacement at joint A.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): Since the column end is fixed, there is no horizontal displacement at joint A.
- Rotation (R): Since the column end is fixed, there is no rotation at joint A.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint A: 0
2. Joint B:
- Vertical Displacement (V): The vertical displacement at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): The horizontal displacement at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Rotation (R): The rotation at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint B: 3
3. Joint C:
- Vertical Displacement (V): The vertical displacement at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): The horizontal displacement at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Rotation (R): The rotation at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint C: 3
4. Joint D:
- Vertical Displacement (V): Since the column end is fixed, there is no vertical displacement at joint D.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): Since the column end is fixed, there is no horizontal displacement at joint D.
- Rotation (R): Since the column end is fixed, there is no rotation at joint D.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint D: 0
Kinematic Indeterminacy Calculation
The kinematic indeterminacy is given by the formula:
I = 3J - 2M - R
where I is the kinematic indeterminacy, J is the number of joints, M is the number of members, and R is the number of support reactions.
In this case, there are no support reactions (R = 0) as the column ends are fixed.
Substituting the values, we have:
I = 3(4)
We are given a single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD with fixed column ends. We need to determine the kinematic indeterminacy of the frame.
Solution
The kinematic indeterminacy of a structure refers to the number of redundant members or joints that can be removed without causing any change in the stability or equilibrium of the structure.
In the given portal frame, the column ends are fixed, which means they are fully restrained against rotation and translation. This implies that there is no relative rotation or displacement between the column ends and the foundation.
Analysis of the Frame
To determine the kinematic indeterminacy, we need to analyze the frame and identify the degrees of freedom.
1. Number of Joints (J): In the given frame, there are four joints: A, B, C, and D.
2. Number of Members (M): There are three members: AB, BC, and CD.
Degree of Freedom Analysis
Next, we analyze the degrees of freedom at each joint to determine the kinematic indeterminacy.
1. Joint A:
- Vertical Displacement (V): Since the column end is fixed, there is no vertical displacement at joint A.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): Since the column end is fixed, there is no horizontal displacement at joint A.
- Rotation (R): Since the column end is fixed, there is no rotation at joint A.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint A: 0
2. Joint B:
- Vertical Displacement (V): The vertical displacement at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): The horizontal displacement at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Rotation (R): The rotation at joint B is not restricted as it is connected to the member AB.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint B: 3
3. Joint C:
- Vertical Displacement (V): The vertical displacement at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): The horizontal displacement at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Rotation (R): The rotation at joint C is not restricted as it is connected to the member BC.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint C: 3
4. Joint D:
- Vertical Displacement (V): Since the column end is fixed, there is no vertical displacement at joint D.
- Horizontal Displacement (H): Since the column end is fixed, there is no horizontal displacement at joint D.
- Rotation (R): Since the column end is fixed, there is no rotation at joint D.
- Total Degrees of Freedom (DOF) at Joint D: 0
Kinematic Indeterminacy Calculation
The kinematic indeterminacy is given by the formula:
I = 3J - 2M - R
where I is the kinematic indeterminacy, J is the number of joints, M is the number of members, and R is the number of support reactions.
In this case, there are no support reactions (R = 0) as the column ends are fixed.
Substituting the values, we have:
I = 3(4)
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fi...
Concept:
kinematic indeterminacy for Rigid jointed plane 2D framed, if axial deformation is neglected
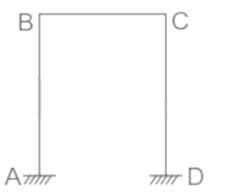
Dk = 3j - R
where j = Number of joints
R = Number of unknown support reactions
where j = 4 , R = 6 , m = 3
Dk = 3×4-6 = 6
If axial deformation is neglected,
Number of inextensible members (For which axial deformation is neglected) = 3
kinematic Indeterminacy = Dk - no of in extensible members = 6 - 3 = 3
Therefore kinematic indeterminacy of a single-bay, single-storeyed portal has its column ends fixed and if axial deformation is neglected is 3.
kinematic indeterminacy for Rigid jointed plane 2D framed, if axial deformation is neglected

Dk = 3j - R
where j = Number of joints
R = Number of unknown support reactions
where j = 4 , R = 6 , m = 3
Dk = 3×4-6 = 6
If axial deformation is neglected,
Number of inextensible members (For which axial deformation is neglected) = 3
kinematic Indeterminacy = Dk - no of in extensible members = 6 - 3 = 3
Therefore kinematic indeterminacy of a single-bay, single-storeyed portal has its column ends fixed and if axial deformation is neglected is 3.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A single-bay, single-storeyed portal frame ABCD has its column ends fixed. If axial deformation is neglected, the kinematic indeterminacy isa)3b)2c)6d)4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















