ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passage and choose the be...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Horses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.
Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.
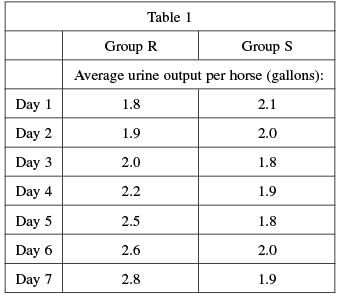
Passage
Horses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.
Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.

Q. Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?
- a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.
- b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.
- c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.
- d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each questio...
Over time, the urinary output for the group that received the supplement increased. According to the passage, increased urination can sometimes lead to dehydration, which supports the statement that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses.
Answer choice C can be eliminated because the table suggests this answer choice is false.
Answer choice C can be eliminated because the table suggests this answer choice is false.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passage and choose the best answer to each question.PassageHorses are susceptible to hoof infections that can seriously impair the horses’ ability to walk. Horse breeders routinely administer dietary supplements in addition to the horses’ regular feed in order to prevent these infections. A side effect of one of the these supplements – supplement X–is increased urination, which can sometimes lead to dehydration in the animal.Twenty (20) adult horses, each weighing approximately 1,000 pounds, were randomly selected and assigned to two groups of 10 horses each. Group R received dietary supplement X while Group S received a placebo (a substance containing no supplement). Each horse in both groups received the same amount of feed and water each day. The horses were placed in individual stalls for 7 days, during which time their urine output was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.Q.Do the results of the study show that dietary supplement X could cause dehydration in horses?a)Yes, because the urinary output increased over time in the group that received the supplement.b)Yes, because the control group maintained a relatively constant urinary output.c)No, because the urinary output stayed the same over time in the group that received the supplement.d)No, because the urinary output of the control group was not adequately measured.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























