Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Dire...
Start Learning for Free
The rated life of a ball bearing varies
- a)Directly as the load
- b)Directly as the square of the load
- c)Directly as the cube of the load
- d)Inversely as the cube of the load
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directl...
Life of a bearing is given by:
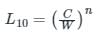
where
L10 = basic life rating in million revolutions
C = dynamic load-carrying capacity
W = equivalent dynamic load
n = constant = 3 for ball bearing and 10/3 for roller bearing
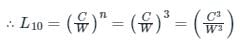
Thus, The rated life of a ball bearing varies Inversely as the cube of the load.
So, option (4) is the correct answer.
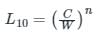
where
L10 = basic life rating in million revolutions
C = dynamic load-carrying capacity
W = equivalent dynamic load
n = constant = 3 for ball bearing and 10/3 for roller bearing
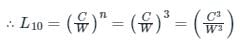
Thus, The rated life of a ball bearing varies Inversely as the cube of the load.
So, option (4) is the correct answer.
Free Test
Community Answer
The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directl...
Rated Life of a Ball Bearing
The rated life of a ball bearing refers to the expected operating life of the bearing under a specific load and speed condition. It is an important parameter to consider when selecting a ball bearing for a particular application. The rated life indicates the number of revolutions or operating hours that the bearing is expected to achieve before showing signs of wear or failure.
Variation of Rated Life with Load
The rated life of a ball bearing is influenced by various factors, including the applied load. The load refers to the force or weight that the bearing is subjected to during operation. It is an important factor that affects the durability and performance of the bearing.
According to the given options, the rated life of a ball bearing varies inversely as the cube of the load. This means that as the load increases, the rated life of the bearing decreases. On the other hand, as the load decreases, the rated life of the bearing increases.
Explanation of Option D: Inversely as the Cube of the Load
The inverse relationship between the rated life and the cube of the load can be understood as follows:
1. Inverse Relationship: The term "inversely" indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. In this case, as the load increases, the rated life decreases, and vice versa.
2. Cube of the Load: The term "cube" refers to raising the load to the power of three. This means that the load is multiplied by itself three times. The cube of the load is a mathematical representation of the load's magnitude.
3. Inverse Cube Relationship: When the rated life varies inversely as the cube of the load, it means that the rated life is inversely proportional to the cube of the load. In other words, if the load is doubled, the rated life will decrease by a factor of eight (2^3 = 8). Similarly, if the load is halved, the rated life will increase by a factor of eight.
Implications of Inverse Cube Relationship
The inverse cube relationship has important implications for the selection and design of ball bearings:
1. Load Capacity: Bearings with higher load capacities are typically more durable and have longer rated lives. Therefore, it is important to consider the expected load conditions when choosing a ball bearing for a specific application.
2. Safety Margin: To ensure a sufficient safety margin, it is advisable to select a ball bearing that can withstand the maximum expected load during operation. This will help prevent premature failure and ensure reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution: Proper load distribution across multiple bearings can help improve the overall durability and reliability of the system. By distributing the load evenly, each individual bearing can operate within its rated capacity, extending the overall system life.
In conclusion, the rated life of a ball bearing varies inversely as the cube of the load. This relationship highlights the importance of considering the load conditions when selecting and designing ball bearings for various applications.
The rated life of a ball bearing refers to the expected operating life of the bearing under a specific load and speed condition. It is an important parameter to consider when selecting a ball bearing for a particular application. The rated life indicates the number of revolutions or operating hours that the bearing is expected to achieve before showing signs of wear or failure.
Variation of Rated Life with Load
The rated life of a ball bearing is influenced by various factors, including the applied load. The load refers to the force or weight that the bearing is subjected to during operation. It is an important factor that affects the durability and performance of the bearing.
According to the given options, the rated life of a ball bearing varies inversely as the cube of the load. This means that as the load increases, the rated life of the bearing decreases. On the other hand, as the load decreases, the rated life of the bearing increases.
Explanation of Option D: Inversely as the Cube of the Load
The inverse relationship between the rated life and the cube of the load can be understood as follows:
1. Inverse Relationship: The term "inversely" indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. In this case, as the load increases, the rated life decreases, and vice versa.
2. Cube of the Load: The term "cube" refers to raising the load to the power of three. This means that the load is multiplied by itself three times. The cube of the load is a mathematical representation of the load's magnitude.
3. Inverse Cube Relationship: When the rated life varies inversely as the cube of the load, it means that the rated life is inversely proportional to the cube of the load. In other words, if the load is doubled, the rated life will decrease by a factor of eight (2^3 = 8). Similarly, if the load is halved, the rated life will increase by a factor of eight.
Implications of Inverse Cube Relationship
The inverse cube relationship has important implications for the selection and design of ball bearings:
1. Load Capacity: Bearings with higher load capacities are typically more durable and have longer rated lives. Therefore, it is important to consider the expected load conditions when choosing a ball bearing for a specific application.
2. Safety Margin: To ensure a sufficient safety margin, it is advisable to select a ball bearing that can withstand the maximum expected load during operation. This will help prevent premature failure and ensure reliable performance.
3. Load Distribution: Proper load distribution across multiple bearings can help improve the overall durability and reliability of the system. By distributing the load evenly, each individual bearing can operate within its rated capacity, extending the overall system life.
In conclusion, the rated life of a ball bearing varies inversely as the cube of the load. This relationship highlights the importance of considering the load conditions when selecting and designing ball bearings for various applications.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The rated life of a ball bearing variesa)Directly as the loadb)Directly as the square of the loadc)Directly as the cube of the loadd)Inversely as the cube of the loadCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























