Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite...
Start Learning for Free
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______
- a)7/27
- b)10/127
- c)19/27
- d)1/3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identical...
Concept:
Binomial distribution
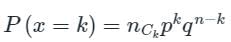
where
p = Probability of success in one trial
q = Probability of failure in one trial = 1 – p
n = Total number of independent trials
k = Discrete random variable
Calculation:
n = 3
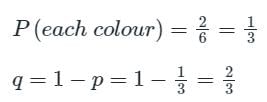
Using binomial distribution
Probability of getting red on the top face at least twice is
P(x ≥ 2) = P(x = 2) + P(x = 3)
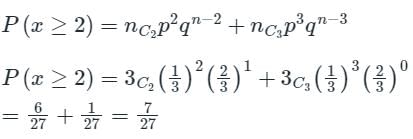
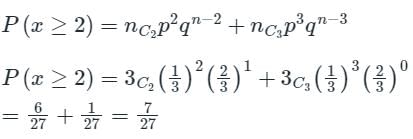
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identical...
To find the probability of obtaining red color on the top face of the dice at least twice, we need to consider the different possible outcomes and count the favorable outcomes.
Given that the dice is unbiased and has three colors (red, blue, and green) such that each color appears only two times on the dice, we can determine the total number of possible outcomes.
Total number of possible outcomes:
Since the dice is cubic, it has 6 faces. There are two colors on each face, so we have 2 choices for each face. Therefore, the total number of possible outcomes is 2^6 = 64.
Now, let's consider the favorable outcomes, i.e., the outcomes where red color appears on the top face at least twice.
Favorable outcomes:
To count the favorable outcomes, we can use the concept of combinations.
Case 1: Red appears on the top face all three times.
In this case, we have only one favorable outcome.
Case 2: Red appears on the top face twice and on one of the other faces once.
To count the number of favorable outcomes, we choose 2 out of 3 throws to have the red color on the top face, and for the remaining throw, we choose any of the other two colors. This can be calculated using combinations as C(3,2) * C(2,1) = 3 * 2 = 6.
Case 3: Red appears on the top face once and on two of the other faces once.
Similar to Case 2, we choose 1 throw to have the red color on the top face and choose any of the other two colors for the remaining two throws. This can be calculated as C(3,1) * C(2,2) = 3 * 1 = 3.
Therefore, the total number of favorable outcomes is 1 + 6 + 3 = 10.
Probability:
The probability of an event is given by the ratio of favorable outcomes to total outcomes.
Probability of obtaining red color on the top face at least twice = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes
= 10 / 64
= 5 / 32
However, this is not one of the given options. Therefore, we need to simplify the fraction.
5 / 32 = 5 / (2^5) = 5 / (2^3 * 2^2) = 5 / (8 * 4) = 5 / 32
The simplified fraction is 5 / 32, which is equivalent to option A: 7/27.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 7/27.
Given that the dice is unbiased and has three colors (red, blue, and green) such that each color appears only two times on the dice, we can determine the total number of possible outcomes.
Total number of possible outcomes:
Since the dice is cubic, it has 6 faces. There are two colors on each face, so we have 2 choices for each face. Therefore, the total number of possible outcomes is 2^6 = 64.
Now, let's consider the favorable outcomes, i.e., the outcomes where red color appears on the top face at least twice.
Favorable outcomes:
To count the favorable outcomes, we can use the concept of combinations.
Case 1: Red appears on the top face all three times.
In this case, we have only one favorable outcome.
Case 2: Red appears on the top face twice and on one of the other faces once.
To count the number of favorable outcomes, we choose 2 out of 3 throws to have the red color on the top face, and for the remaining throw, we choose any of the other two colors. This can be calculated using combinations as C(3,2) * C(2,1) = 3 * 2 = 6.
Case 3: Red appears on the top face once and on two of the other faces once.
Similar to Case 2, we choose 1 throw to have the red color on the top face and choose any of the other two colors for the remaining two throws. This can be calculated as C(3,1) * C(2,2) = 3 * 1 = 3.
Therefore, the total number of favorable outcomes is 1 + 6 + 3 = 10.
Probability:
The probability of an event is given by the ratio of favorable outcomes to total outcomes.
Probability of obtaining red color on the top face at least twice = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes
= 10 / 64
= 5 / 32
However, this is not one of the given options. Therefore, we need to simplify the fraction.
5 / 32 = 5 / (2^5) = 5 / (2^3 * 2^2) = 5 / (8 * 4) = 5 / 32
The simplified fraction is 5 / 32, which is equivalent to option A: 7/27.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 7/27.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider an unbiased cubic dice with opposite faces coloured identically and each face coloured red, blue or green such that each colour appears only two times on the dice. If the dice is thrown thrice, the probability of obtaining red colour on top face of the dice at least twice is _______a)7/27b)10/127c)19/27d)1/3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























