Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > What are the effects of price floor?
Start Learning for Free
What are the effects of price floor?
Most Upvoted Answer
What are the effects of price floor?
Effects of price floor on the market of a good: A minimum price is fixed which the traders must pay the farmers in the wholesale market. But the traders may not buy wheat at all. Often the Government offers ‘support price’ to the farmers. It is a price which corresponds to the minimum price but implies that the Government would buy the entire surplus of the farmers’ produce which they fail to sell in the open market at the floor price.
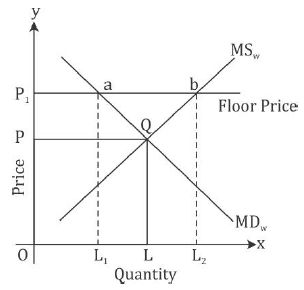
MDw and MSw are the curves showing market demand for wheat and market supply of wheat. Q indicates the point of equilibrium. OP indicates the equilibrium price and OL the equilibrium quantity of wheat. Considering the fact that the equilibrium price may be considerably low for the farmers and the fact that their income should be regulated, the Government fixes OP1 as the floor price. Traders in the market are bound to pay at least OP1 price for the purchase of wheat. However, rise in prices reduces the demand from OL to OL1. On the other hand, market supply expands from OL to OL2. There emerges excess supply = ab. The Government purchases the excess supply and stores it as buffer stocks. Hence, the Government has to bear the social cost of floor price and support price to protect the farmers’ interest.
Community Answer
What are the effects of price floor?
Effects of Price Floor
Price floor is a government-imposed minimum price that is set above the equilibrium price in a market. It is typically implemented to protect producers and workers by ensuring they receive fair compensation for their goods or services. However, price floors can have both positive and negative effects on the market, which are discussed in detail below.
1. Surplus of Supply
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, it creates a surplus of supply. This occurs because the price floor prevents the market from reaching its natural equilibrium, causing producers to supply more goods or services than consumers demand at the higher price. As a result, excess supply accumulates, leading to a surplus in the market.
2. Reduced Quantity Demanded
Due to the higher price resulting from a price floor, the quantity demanded by consumers tends to decrease. This happens as consumers are deterred from purchasing the product or service at the elevated price, especially if there are readily available substitutes in the market. Consequently, the demand for the good or service decreases.
3. Inefficient Allocation of Resources
Price floors can lead to an inefficient allocation of resources within the market. Since the price is artificially inflated, resources may be misallocated towards the production of the goods or services affected by the price floor. This can result in a diversion of resources from more efficient uses, leading to a loss in overall economic welfare.
4. Increased Production Costs
For producers, a price floor can lead to increased production costs. In order to maintain the higher price, producers may have to incur additional expenses, such as higher wages or raw material costs. This can reduce the profitability of businesses and hinder their ability to compete in the market.
5. Income Redistribution
One of the intended effects of a price floor is to redistribute income from consumers to producers or workers. By setting a minimum price, the government aims to ensure that producers receive a fair income for their products or services. This can benefit certain groups, such as small-scale farmers or low-wage workers, who may rely on the price floor for their livelihoods.
6. Potential for Black Markets
In some cases, price floors can create incentives for the emergence of black markets. When the government sets a price floor above the equilibrium, it creates a price differential that encourages illegal activities, such as selling goods or services below the legal price. This undermines the effectiveness of the price floor and can lead to market distortions.
In conclusion, price floors have both positive and negative effects on the market. While they can protect producers and workers by ensuring fair compensation, they can also result in surpluses, reduced quantity demanded, inefficient resource allocation, increased production costs, income redistribution, and the potential for black markets. It is crucial for policymakers to carefully consider these effects and weigh the benefits against the drawbacks before implementing price floors.
Price floor is a government-imposed minimum price that is set above the equilibrium price in a market. It is typically implemented to protect producers and workers by ensuring they receive fair compensation for their goods or services. However, price floors can have both positive and negative effects on the market, which are discussed in detail below.
1. Surplus of Supply
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, it creates a surplus of supply. This occurs because the price floor prevents the market from reaching its natural equilibrium, causing producers to supply more goods or services than consumers demand at the higher price. As a result, excess supply accumulates, leading to a surplus in the market.
2. Reduced Quantity Demanded
Due to the higher price resulting from a price floor, the quantity demanded by consumers tends to decrease. This happens as consumers are deterred from purchasing the product or service at the elevated price, especially if there are readily available substitutes in the market. Consequently, the demand for the good or service decreases.
3. Inefficient Allocation of Resources
Price floors can lead to an inefficient allocation of resources within the market. Since the price is artificially inflated, resources may be misallocated towards the production of the goods or services affected by the price floor. This can result in a diversion of resources from more efficient uses, leading to a loss in overall economic welfare.
4. Increased Production Costs
For producers, a price floor can lead to increased production costs. In order to maintain the higher price, producers may have to incur additional expenses, such as higher wages or raw material costs. This can reduce the profitability of businesses and hinder their ability to compete in the market.
5. Income Redistribution
One of the intended effects of a price floor is to redistribute income from consumers to producers or workers. By setting a minimum price, the government aims to ensure that producers receive a fair income for their products or services. This can benefit certain groups, such as small-scale farmers or low-wage workers, who may rely on the price floor for their livelihoods.
6. Potential for Black Markets
In some cases, price floors can create incentives for the emergence of black markets. When the government sets a price floor above the equilibrium, it creates a price differential that encourages illegal activities, such as selling goods or services below the legal price. This undermines the effectiveness of the price floor and can lead to market distortions.
In conclusion, price floors have both positive and negative effects on the market. While they can protect producers and workers by ensuring fair compensation, they can also result in surpluses, reduced quantity demanded, inefficient resource allocation, increased production costs, income redistribution, and the potential for black markets. It is crucial for policymakers to carefully consider these effects and weigh the benefits against the drawbacks before implementing price floors.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Question Description
What are the effects of price floor? for Commerce 2025 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about What are the effects of price floor? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What are the effects of price floor?.
What are the effects of price floor? for Commerce 2025 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about What are the effects of price floor? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What are the effects of price floor?.
Solutions for What are the effects of price floor? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What are the effects of price floor? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What are the effects of price floor?, a detailed solution for What are the effects of price floor? has been provided alongside types of What are the effects of price floor? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What are the effects of price floor? tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















