ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions: Read the passages and choose the ...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Gregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.
If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.
It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).
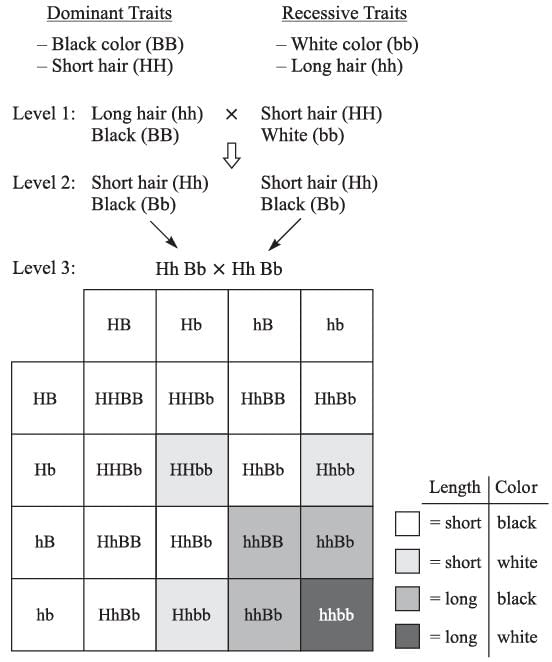
A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.
Passage
Gregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.
If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.
It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).
A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.

Q. Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?
- a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.
- b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.
- c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.
- d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each quest...
The best answer is C. If heterozygous rabbits are bred (level 2), it is possible for the recessive traits to be visible in the immediate generation, because it is possible for an offspring to receive two recessive alleles. This is also true for future generations, making answer choice C the best answer.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all ACT courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all ACT courses

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageGregor Mendel is known for his work in genetics. He is credited with discovering how traits (characteristics) are passed from one generation to the next. After his observations of inherited traits, Mendel concluded that each organism carries two sets of information about a certain trait.If the two sets differ about the same trait, one set dominates the other. That way, information can be passed on through the generations, even if the trait is not expressed.It has since been determined that the presence of certain traits is attributed to genes, and the different forms that genes can take, known as alleles. Dominant alleles (D) produce dominant characteristics; recessive alleles (d ) produce recessive charactersitics. Dominant alleles are expressed whenever present (DD, Dd) but recessive alleles are expressed only when the dominant allele is absent (dd).A study was done in which the independence of two traits was tested. In this study, a rabbit with long black hair was mated with a rabbit with short white hair. The dominant trait for hair length is short (H). The dominant trait for hair color is black (B). If the two initial rabbits (level 1 in the figure below) are homozygous for their traits, meaning that the two alleles for each trait are the same, breeding them will result in offspring that have both a dominant and recessive allele for each trait. Such a pairing of alleles is known as heterozygous. If, as in level 2 of the figure, two heterozygous rabbits are bred, the chart (level 3) contains all the possibilities for their offspring.Q.Which of the following statements might be a reasonable generalization made after examining this study?a)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not be visible in the immediate generation, but may be visible in the second generation.b)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits might be visible in the immediate generation, but will not be visible in the second generation.c)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will be visible in the immediate generation and in the second generation.d)If heterozygous rabbits with opposite traits are bred, the recessive traits will not at all be visible in future generations because they are overcome by the dominant traits.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























