ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions: Read the passages and choose the ...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
A chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).
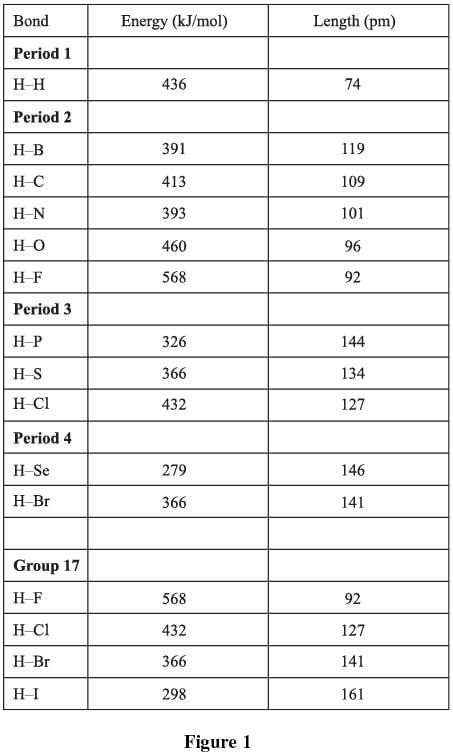
When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.
Passage
A chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).
When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.

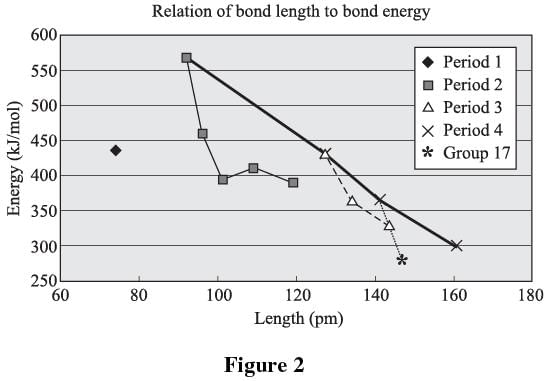
Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).

Q. Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.
Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?
Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?
- a)H and C
- b)H and O
- c)H and P
- d)H and S
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each quest...
The best answer is b. According to Figure 1, the only pair of elements in the answer choices with a bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol is H and O (460 kJ/mol), answer choice b.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageA chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through both sharing and exchanging of electrons or electrostatic forces. Bond energy is a measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. For example, the carbon hydrogen (C–H) bond energy is the energy change involved with breaking up the bond between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Bonds with a higher energy release more energy when they form, and are considered to be more stable (less reactive).When reacting with nonmetals, hydrogen forms covalent bonds, meaning that the bonded atoms share electrons with each other. Figure 1 shows the bond energies and distances for bonds involving hydrogen and nonmetals (H–X). The chart is arranged by period (rows of periodic table); in addition, the values for group 17 (column 17 on the periodic table) are compared.Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond lengths are measured in molecules by means of X-ray diffraction. A set of two atoms sharing a bond is unique going from one molecule to the next. For example, the oxygen to hydrogen bond in water is different from the oxygen to hydrogen bond in alcohol. It is, however, possible to make generalizations when the general structure is the same. Figure 2 relates bond energy to bond length for H–X bonds between hydrogen and nonmetals. The elements in each period or group are connected by a line (with the exception of the first, which contains only hydrogen).Q.Suppose a certain experiment calls for a very stable substance with bond energy greater than 420 kJ/mol.Which of the following pairs of elements in a compound would yield a stable enough substance?a)H and Cb)H and Oc)H and Pd)H and SCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























