Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Which of the following voltage ranges is corr...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?
- a)High voltage
- b)Very high voltage
- c)Low voltage
- d)Medium voltage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum ci...
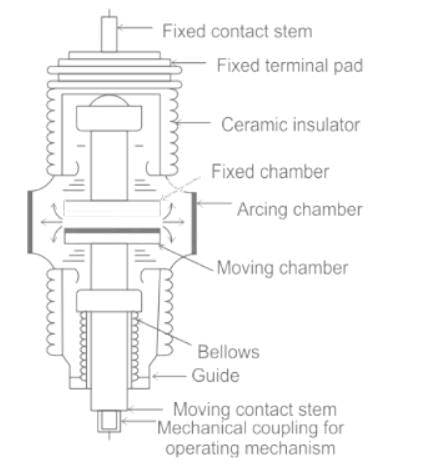
Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- A vacuum circuit breaker is a kind of circuit breaker where the arc quenching takes place in a vacuum medium.
- A vacuum that is used as the arc quenching medium in a circuit breaker is known as a vacuum circuit breaker because a vacuum gives high insulating strength due to superior arc quenching properties.
- Alloys like Copper-bismuth, silver-tellurium and copper-lead are the ideal materials to make VCB contacts.
- It is mainly used for medium voltage ranging from 11 KV to 33 KV.
- When the fault occurs in the system, the contacts of the breaker are moved apart and hence the arc is developed between them.
- When the current-carrying contacts are pulled apart, the temperature of their connecting parts is very high due to which ionization occurs.
- Due to the ionization, the contact space is filled with the vapour of positive ions which is discharged from the contact material.
- The density of vapour depends on the current in the arcing. Due to the decreasing mode of the current wave their rate of release of vapour falls and after the current zero, the medium regains its dielectric strength provided vapour density around the contacts is reduced.
- Hence, the arc does not restrike again because the metal vapour is quickly removed from the contact zone.
Additional Information
Vacuum Circuit Breaker:
Vacuum Circuit Breaker:
- A vacuum circuit breaker is a kind of circuit breaker where the arc quenching takes place in a vacuum medium.
- The operation of opening and closing of current carrying contacts and associated arc interruption take place in a vacuum chamber in the breaker which is called a vacuum interrupter.
- Vacuum circuit breakers are more commonly used at system voltage levels up to 72 kV.
- The vacuum contactor’s rated 1.2/3.6/7.2 kV is used for indoor metal enclosed control gear.
- The vacuum interrupters rated 3.6/7.2/12/36 kV is used for indoor metal-clad switch gear.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum ci...
Understanding Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Vacuum circuit breakers (VCBs) are crucial components in electrical systems, primarily used for switching and protecting electrical circuits. Their operation relies on the vacuum environment within the contacts to extinguish the arc generated during switching.
Voltage Classification
- High Voltage: Generally refers to voltages above 1 kV and up to 100 kV. While VCBs can be used in some high-voltage applications, they are not the predominant choice.
- Very High Voltage: This typically involves voltages above 100 kV. VCBs are generally not designed for these levels due to the significant challenges in arc extinction.
- Low Voltage: This category usually includes voltages below 1 kV. Although VCBs can operate in low voltage applications, they are not commonly utilized in that range.
- Medium Voltage: This is the most suitable range for VCBs, typically encompassing voltages from 1 kV to 36 kV. They are specifically designed for this voltage range, offering efficient switching capabilities and effective arc extinction.
Why Medium Voltage?
- Arc Quenching: The vacuum environment allows for rapid quenching of the arc, making VCBs effective in medium voltage applications where quick response is crucial.
- Compact Design: VCBs are smaller and lighter than other types of breakers, making them ideal for medium voltage installations.
- Reliability: They provide high reliability and require less maintenance compared to other circuit breakers, making them cost-effective for medium voltage systems.
In conclusion, the correct voltage range for using a vacuum circuit breaker is indeed medium voltage (option D), as they are specifically engineered to operate effectively within this range.
Vacuum circuit breakers (VCBs) are crucial components in electrical systems, primarily used for switching and protecting electrical circuits. Their operation relies on the vacuum environment within the contacts to extinguish the arc generated during switching.
Voltage Classification
- High Voltage: Generally refers to voltages above 1 kV and up to 100 kV. While VCBs can be used in some high-voltage applications, they are not the predominant choice.
- Very High Voltage: This typically involves voltages above 100 kV. VCBs are generally not designed for these levels due to the significant challenges in arc extinction.
- Low Voltage: This category usually includes voltages below 1 kV. Although VCBs can operate in low voltage applications, they are not commonly utilized in that range.
- Medium Voltage: This is the most suitable range for VCBs, typically encompassing voltages from 1 kV to 36 kV. They are specifically designed for this voltage range, offering efficient switching capabilities and effective arc extinction.
Why Medium Voltage?
- Arc Quenching: The vacuum environment allows for rapid quenching of the arc, making VCBs effective in medium voltage applications where quick response is crucial.
- Compact Design: VCBs are smaller and lighter than other types of breakers, making them ideal for medium voltage installations.
- Reliability: They provide high reliability and require less maintenance compared to other circuit breakers, making them cost-effective for medium voltage systems.
In conclusion, the correct voltage range for using a vacuum circuit breaker is indeed medium voltage (option D), as they are specifically engineered to operate effectively within this range.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?a)High voltageb)Very high voltagec)Low voltaged)Medium voltageCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























