Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A buck converter is used to control a d.c. mo...
Start Learning for Free
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.
- a)60%
- b)50%
- c)35%
- d)75%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc bu...
Concept:
In a buck converter (step down chopper)
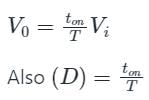
Where,
D = Duty ratio
V0 = Average out-put voltage or DC output voltage
Vi = Input voltage
ton = On time period
T = total time period
Calculation:
V0 = 150 V, Vi = 200 V
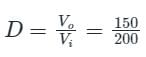
D = 0.75 = 75%
Note:
RMS output voltage of buck converter is given by
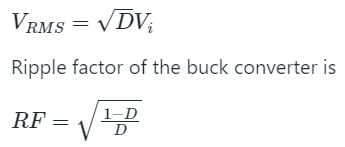
Most Upvoted Answer
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc bu...
Understanding Buck Converter Operation
A buck converter steps down voltage from a higher level to a lower level. The output voltage (Vout) is controlled by the duty ratio (D), which is the fraction of time the switch is ON during one complete cycle.
Formula for Duty Ratio
The relationship between input voltage (Vin), output voltage (Vout), and duty ratio (D) is given by the formula:
Vout = D * Vin
To find the duty ratio, we can rearrange this formula:
D = Vout / Vin
Given Values
- Input Voltage, Vin = 200 V
- Desired Output Voltage, Vout = 150 V
Calculating Duty Ratio
Substituting the given values into the rearranged formula:
D = 150 V / 200 V
D = 0.75
Converting to Percentage
To express the duty ratio as a percentage, multiply by 100:
D = 0.75 * 100 = 75%
Conclusion
The required duty ratio to produce 150 V across the DC motor when the input voltage is 200 V is 75%. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (75%).
This calculation demonstrates how the duty cycle directly influences the output voltage in a buck converter, making it a crucial factor in motor control applications.
A buck converter steps down voltage from a higher level to a lower level. The output voltage (Vout) is controlled by the duty ratio (D), which is the fraction of time the switch is ON during one complete cycle.
Formula for Duty Ratio
The relationship between input voltage (Vin), output voltage (Vout), and duty ratio (D) is given by the formula:
Vout = D * Vin
To find the duty ratio, we can rearrange this formula:
D = Vout / Vin
Given Values
- Input Voltage, Vin = 200 V
- Desired Output Voltage, Vout = 150 V
Calculating Duty Ratio
Substituting the given values into the rearranged formula:
D = 150 V / 200 V
D = 0.75
Converting to Percentage
To express the duty ratio as a percentage, multiply by 100:
D = 0.75 * 100 = 75%
Conclusion
The required duty ratio to produce 150 V across the DC motor when the input voltage is 200 V is 75%. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (75%).
This calculation demonstrates how the duty cycle directly influences the output voltage in a buck converter, making it a crucial factor in motor control applications.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.a)60%b)50%c)35%d)75%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















