Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > The maximum rate at which nearly error-free d...
Start Learning for Free
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined as
- a)Modulation
- b)Signal to Noise Ratio
- c)Frequency Bandwidth
- d)Channel Capacity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically ...
- Channel capacity is the maximum rate at which the data can be transmitted through a channel without errors.
- The capacity of a channel can be increased by increasing channel bandwidth as well as by increasing signal to noise ratio.
- Channel capacity (C) is given as,
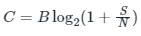
Where,
B: Bandwidth
S/N: Signal to noise ratio
Entropy:
The entropy of a probability distribution is the average or the amount of information when drawing from a probability distribution.
It is calculated as:
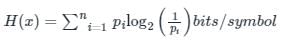
pi is the probability of the occurrence of a symbol.
B: Bandwidth
S/N: Signal to noise ratio
Entropy:
The entropy of a probability distribution is the average or the amount of information when drawing from a probability distribution.
It is calculated as:
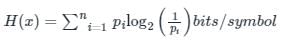
pi is the probability of the occurrence of a symbol.
Most Upvoted Answer
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically ...
Introduction:
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is known as the channel capacity. It represents the upper limit of data transmission and is influenced by various factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth.
Explanation:
Modulation:
Modulation refers to the process of encoding information onto a carrier signal. It allows the transmission of data by varying the characteristics of the carrier signal, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase. While modulation techniques play a crucial role in data transmission, they do not directly determine the maximum achievable data rate.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio:
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure of the strength of the desired signal compared to the level of background noise. A higher SNR indicates a better quality signal. In communication systems, a higher SNR allows for more reliable transmission and reduces the likelihood of errors. However, SNR alone cannot determine the maximum data rate.
Frequency Bandwidth:
Frequency bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies available for communication in a channel. A wider bandwidth allows for a greater amount of data to be transmitted simultaneously, resulting in a higher data rate. However, the frequency bandwidth alone does not determine the maximum achievable data rate.
Channel Capacity:
The channel capacity is the maximum data rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. It takes into account various factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth. The Shannon Capacity Formula, developed by Claude Shannon, provides a theoretical upper bound on the channel capacity. It states that the channel capacity is equal to the bandwidth multiplied by the logarithm of one plus the signal-to-noise ratio (C = B log2(1+SNR)).
The channel capacity is a measure of the channel's ability to transmit information without errors. It represents the maximum achievable data rate under ideal conditions. Achieving a data rate close to the channel capacity requires advanced modulation techniques, efficient error-correction coding, and signal processing algorithms.
In conclusion, the maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined as the channel capacity. It is determined by factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth. The channel capacity represents the upper limit of data transmission and can be calculated using the Shannon Capacity Formula.
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is known as the channel capacity. It represents the upper limit of data transmission and is influenced by various factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth.
Explanation:
Modulation:
Modulation refers to the process of encoding information onto a carrier signal. It allows the transmission of data by varying the characteristics of the carrier signal, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase. While modulation techniques play a crucial role in data transmission, they do not directly determine the maximum achievable data rate.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio:
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure of the strength of the desired signal compared to the level of background noise. A higher SNR indicates a better quality signal. In communication systems, a higher SNR allows for more reliable transmission and reduces the likelihood of errors. However, SNR alone cannot determine the maximum data rate.
Frequency Bandwidth:
Frequency bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies available for communication in a channel. A wider bandwidth allows for a greater amount of data to be transmitted simultaneously, resulting in a higher data rate. However, the frequency bandwidth alone does not determine the maximum achievable data rate.
Channel Capacity:
The channel capacity is the maximum data rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. It takes into account various factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth. The Shannon Capacity Formula, developed by Claude Shannon, provides a theoretical upper bound on the channel capacity. It states that the channel capacity is equal to the bandwidth multiplied by the logarithm of one plus the signal-to-noise ratio (C = B log2(1+SNR)).
The channel capacity is a measure of the channel's ability to transmit information without errors. It represents the maximum achievable data rate under ideal conditions. Achieving a data rate close to the channel capacity requires advanced modulation techniques, efficient error-correction coding, and signal processing algorithms.
In conclusion, the maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined as the channel capacity. It is determined by factors such as modulation, signal-to-noise ratio, and frequency bandwidth. The channel capacity represents the upper limit of data transmission and can be calculated using the Shannon Capacity Formula.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The maximum rate at which nearly error-free data can be theoretically transmitted over a communication channel is defined asa)Modulationb)Signal to Noise Ratioc)Frequency Bandwidthd)Channel CapacityCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















