Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Reactive power requirement of a power transmi...
Start Learning for Free
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __
- a)Power angle δ
- b)|Vs|-|Vr|
- c)Vs
- d)Vr
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on _...
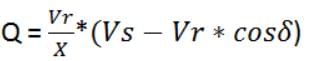
Most Upvoted Answer
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on _...
Understanding Reactive Power in Transmission Systems
Reactive power is a crucial aspect of power transmission systems, influencing stability and efficiency. It is primarily determined by the voltage magnitudes at both the sending and receiving ends of the transmission line.
Key Factors Influencing Reactive Power
- Voltage Magnitudes: The difference in voltage magnitudes between the sending end (Vs) and the receiving end (Vr) significantly impacts reactive power requirements. The relationship can be summarized as follows:
- Reactive power (Q) is affected by |Vs| - |Vr|, where |Vs| and |Vr| are the respective magnitudes of the sending and receiving voltages.
- Power Angle (δ): Although the power angle (δ) does play a role in the active power flow, it is not the primary determinant of reactive power. δ primarily affects the real power transfer rather than the reactive component.
- Voltage Levels: Higher voltage levels at the sending end can reduce the overall reactive power requirement, as they improve the ability to transmit power over long distances with less loss.
Conclusion
The correct answer being option 'B' emphasizes the significance of the voltage difference in determining reactive power requirements. In summary, reactive power is predominantly influenced by the magnitudes of the sending and receiving voltages, making |Vs| - |Vr| a critical factor in power transmission systems. Understanding this relationship is essential for engineers to ensure efficient and stable operation of electrical networks.
Reactive power is a crucial aspect of power transmission systems, influencing stability and efficiency. It is primarily determined by the voltage magnitudes at both the sending and receiving ends of the transmission line.
Key Factors Influencing Reactive Power
- Voltage Magnitudes: The difference in voltage magnitudes between the sending end (Vs) and the receiving end (Vr) significantly impacts reactive power requirements. The relationship can be summarized as follows:
- Reactive power (Q) is affected by |Vs| - |Vr|, where |Vs| and |Vr| are the respective magnitudes of the sending and receiving voltages.
- Power Angle (δ): Although the power angle (δ) does play a role in the active power flow, it is not the primary determinant of reactive power. δ primarily affects the real power transfer rather than the reactive component.
- Voltage Levels: Higher voltage levels at the sending end can reduce the overall reactive power requirement, as they improve the ability to transmit power over long distances with less loss.
Conclusion
The correct answer being option 'B' emphasizes the significance of the voltage difference in determining reactive power requirements. In summary, reactive power is predominantly influenced by the magnitudes of the sending and receiving voltages, making |Vs| - |Vr| a critical factor in power transmission systems. Understanding this relationship is essential for engineers to ensure efficient and stable operation of electrical networks.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Reactive power requirement of a power transmission system depends on __a)Power angle δb)|Vs|-|Vr|c)Vsd)VrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























