Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > What is the name of the process in which redu...
Start Learning for Free
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?
- a)Chlorination
- b)Hydrogenation
- c)Dechlorination
- d)Sulphurification
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sul...
Chlorination:
Chlorination is used for: Disinfection, control of microorganisms, removal of ammonia, control of taste and odour, destruction of organic matter, hydrogen sulphide oxidation.
Types of chlorination:
1. Plain chlorination:
This term is used to indicate that only the chlorine treatment and no other treatment has been given to the raw water
It is used for clean water, i.e turbidity between 20 - 30 mg/l
Dose is 0.5 mg/l
2. Pre-chlorination:
It is the process of applying chlorine to the water before filtration or rather before sedimentation and coagulation.
Normal dose is 5 to 10 mg/l and pre-chlorination is always followed by post chlorination
3. Post chlorination:
It is the normal standard process of applying chlorine in the end, when all other treatments have been completed.
4. Double chlorination:
It simply means that the water has been chlorinated twice
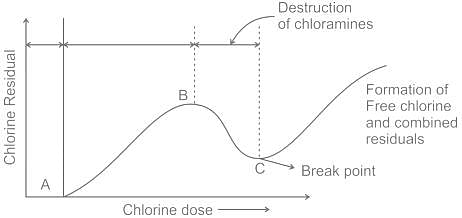
5. Break-point chlorination
It means an extent of chlorine is added to water.
It represents that much dose of chlorination, beyond which any further additional chlorine will appear as free residual chlorine.
6. Super chlorination
When excess chlorine is added to water during epidemic such that it gives a residual of 1 to 2 mg/l beyond break point is called as super chlorination.
7. Dechlorination
When chlorine residue is high, excess chlorine will be removed by dechlorinating agent.
The various dechlorinating agents are:
(i) Sodium Thiosulphate (Na2S2O3H2O)
(ii) Activated carbon
(iii) Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
(iv) Sodium bisulphate (NaHSO3)
(v) Ammonia as NH4OH
(vi) Sodium sulphate (Na2S2O3)
Chlorination is used for: Disinfection, control of microorganisms, removal of ammonia, control of taste and odour, destruction of organic matter, hydrogen sulphide oxidation.
Types of chlorination:

1. Plain chlorination:
This term is used to indicate that only the chlorine treatment and no other treatment has been given to the raw water
It is used for clean water, i.e turbidity between 20 - 30 mg/l
Dose is 0.5 mg/l
2. Pre-chlorination:
It is the process of applying chlorine to the water before filtration or rather before sedimentation and coagulation.
Normal dose is 5 to 10 mg/l and pre-chlorination is always followed by post chlorination
3. Post chlorination:
It is the normal standard process of applying chlorine in the end, when all other treatments have been completed.
4. Double chlorination:
It simply means that the water has been chlorinated twice
5. Break-point chlorination
It means an extent of chlorine is added to water.
It represents that much dose of chlorination, beyond which any further additional chlorine will appear as free residual chlorine.
6. Super chlorination
When excess chlorine is added to water during epidemic such that it gives a residual of 1 to 2 mg/l beyond break point is called as super chlorination.
7. Dechlorination
When chlorine residue is high, excess chlorine will be removed by dechlorinating agent.
The various dechlorinating agents are:
(i) Sodium Thiosulphate (Na2S2O3H2O)
(ii) Activated carbon
(iii) Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
(iv) Sodium bisulphate (NaHSO3)
(v) Ammonia as NH4OH
(vi) Sodium sulphate (Na2S2O3)
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the name of the process in which reducing chemical such as sulphur dioxide (SO2), sodium trisulphite (NaHSO3) and sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is added to remove unwanted residual of chlorine from water?a)Chlorinationb)Hydrogenationc)Dechlorinationd)SulphurificationCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























