UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso...
Start Learning for Free
Silicates with continuous 3D frame work
- a)Neso-silicates
- b)Soro-silicates
- c)Phyllo-silicates
- d)Tecto-silicates
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicate...
Tecto-silicates have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with all the four oxygen atoms of each tetrahedron being shared with other tetrahedra. This results in an overall silicon-to-oxygen ratio of 1:2. Examples include quartz and feldspars.
As for the other categories:
Neso-silicates or orthosilicates consist of independent silicate tetrahedrons (SiO4)4- that are separated by metal cations. Olivine is an example.
Soro-silicates (or double-island silicates) involve two isolated silicate tetrahedrons connected together. Axinite is an example of a sorosilicate.
Phyllo-silicates or sheet silicates are structured in layers or sheets. Micas like biotite and muscovite, and clays like kaolinite, are examples.
Nesosilicates (Island Silicates)
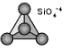
If the corner oxygens are not shared with other SiO4-4 tetrahedrons, each tetrahedron will be isolated. Thus, this group is often referred to as the island silicate group. The basic structural unit is then SiO4-4. In this group the oxygens are shared with octahedral groups that contain other cations like Mg+2, Fe+2, or Ca+2. Olivine is a good example: (Mg,Fe)2SiO4.
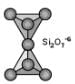
Sorosilicates (Double Island Silicates)
If one of the corner oxygens is shared with another tetrahedron, this gives rise to the sorosilicate group. It is often referred to as the double island group because there are two linked tetrahedrons isolated from all other tetrahedrons. In this case, the basic structural unit is Si2O7-6. A good example of a sorosilicate is the mineral hemimorphite - Zn4Si2O7(OH).H2O. Some sorosilicates are a combination of single and double islands, like in epidote - Ca2(Fe+3,Al)Al2(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH).
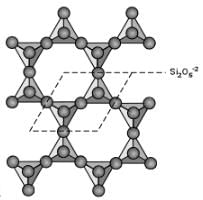
Phyllosilicates (Sheet Silicates)
If 3 of the oxygens from each tetrahedral group are shared such that an infinite sheet of SiO4 tetrahedra are shared we get the basis for the phyllosilicates or sheet silicates. In this case the basic structural group is Si2O5-2. The micas, clay minerals, chlorite, talc, and serpentine minerals are all based on this structure. A good example is biotite - K(Mg,Fe)3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2. Note that in this structure, Al is substituting for Si in one of the tetrahedral groups.
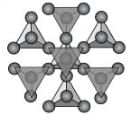
Tectosilicates (Framework Silicates)
If all of the corner oxygens are shared with another SiO4 tetrahedron, then a framework structure develops. The basic structural group then becomes SiO2. The minerals quartz, cristobalite, and tridymite all are based on this structure. If some of the Si+4 ions are replaced by Al+3 then this produces a charge imbalance and allows for other ions to be found coordinated in different arrangements within the framework structure. Thus, the feldspar and feldspathoid minerals are also based on the tectosilicate framework
So, Silicates with continuous 3D frame work is Tectosilicates.
As for the other categories:
Neso-silicates or orthosilicates consist of independent silicate tetrahedrons (SiO4)4- that are separated by metal cations. Olivine is an example.
Soro-silicates (or double-island silicates) involve two isolated silicate tetrahedrons connected together. Axinite is an example of a sorosilicate.
Phyllo-silicates or sheet silicates are structured in layers or sheets. Micas like biotite and muscovite, and clays like kaolinite, are examples.
Nesosilicates (Island Silicates)
If the corner oxygens are not shared with other SiO4-4 tetrahedrons, each tetrahedron will be isolated. Thus, this group is often referred to as the island silicate group. The basic structural unit is then SiO4-4. In this group the oxygens are shared with octahedral groups that contain other cations like Mg+2, Fe+2, or Ca+2. Olivine is a good example: (Mg,Fe)2SiO4.

Sorosilicates (Double Island Silicates)
If one of the corner oxygens is shared with another tetrahedron, this gives rise to the sorosilicate group. It is often referred to as the double island group because there are two linked tetrahedrons isolated from all other tetrahedrons. In this case, the basic structural unit is Si2O7-6. A good example of a sorosilicate is the mineral hemimorphite - Zn4Si2O7(OH).H2O. Some sorosilicates are a combination of single and double islands, like in epidote - Ca2(Fe+3,Al)Al2(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH).

Phyllosilicates (Sheet Silicates)
If 3 of the oxygens from each tetrahedral group are shared such that an infinite sheet of SiO4 tetrahedra are shared we get the basis for the phyllosilicates or sheet silicates. In this case the basic structural group is Si2O5-2. The micas, clay minerals, chlorite, talc, and serpentine minerals are all based on this structure. A good example is biotite - K(Mg,Fe)3(AlSi3)O10(OH)2. Note that in this structure, Al is substituting for Si in one of the tetrahedral groups.

Tectosilicates (Framework Silicates)
If all of the corner oxygens are shared with another SiO4 tetrahedron, then a framework structure develops. The basic structural group then becomes SiO2. The minerals quartz, cristobalite, and tridymite all are based on this structure. If some of the Si+4 ions are replaced by Al+3 then this produces a charge imbalance and allows for other ions to be found coordinated in different arrangements within the framework structure. Thus, the feldspar and feldspathoid minerals are also based on the tectosilicate framework

So, Silicates with continuous 3D frame work is Tectosilicates.
Most Upvoted Answer
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicate...
Tecto-silicates:
Tecto-silicates are silicate minerals that have a continuous three-dimensional framework structure. This means that the silicon-oxygen tetrahedra are interconnected in all directions, forming a solid framework.
Characteristics of Tecto-silicates:
- Tecto-silicates have a high degree of polymerization, with each tetrahedron sharing all of its oxygen atoms with neighboring tetrahedra.
- These minerals have a high density and hardness due to their tightly packed structure.
- Tecto-silicates are typically insoluble in water and have a low reactivity compared to other silicate groups.
Examples of Tecto-silicates:
- Quartz: Quartz is one of the most common tecto-silicates, known for its hexagonal crystal structure and wide range of colors.
- Feldspar: Feldspar is another important tecto-silicate mineral group, often found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
- Zeolites: Zeolites are tecto-silicates with a porous structure, used in industrial applications such as water softening and gas separation.
Importance of Tecto-silicates:
- Tecto-silicates make up a large portion of the Earth's crust and play a critical role in the formation of rocks and minerals.
- These minerals have economic significance, as they are used in construction, ceramics, and other industrial applications.
- Understanding the properties and structures of tecto-silicates is essential for geologists and mineralogists studying the Earth's composition and history.
Tecto-silicates are silicate minerals that have a continuous three-dimensional framework structure. This means that the silicon-oxygen tetrahedra are interconnected in all directions, forming a solid framework.
Characteristics of Tecto-silicates:
- Tecto-silicates have a high degree of polymerization, with each tetrahedron sharing all of its oxygen atoms with neighboring tetrahedra.
- These minerals have a high density and hardness due to their tightly packed structure.
- Tecto-silicates are typically insoluble in water and have a low reactivity compared to other silicate groups.
Examples of Tecto-silicates:
- Quartz: Quartz is one of the most common tecto-silicates, known for its hexagonal crystal structure and wide range of colors.
- Feldspar: Feldspar is another important tecto-silicate mineral group, often found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
- Zeolites: Zeolites are tecto-silicates with a porous structure, used in industrial applications such as water softening and gas separation.
Importance of Tecto-silicates:
- Tecto-silicates make up a large portion of the Earth's crust and play a critical role in the formation of rocks and minerals.
- These minerals have economic significance, as they are used in construction, ceramics, and other industrial applications.
- Understanding the properties and structures of tecto-silicates is essential for geologists and mineralogists studying the Earth's composition and history.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Similar UGC NET Doubts
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Silicates with continuous 3D frame worka)Neso-silicatesb)Soro-silicatesc)Phyllo-silicatesd)Tecto-silicatesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























