UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluor...
Start Learning for Free
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies
- a)increase in symmetry and bond elongation
- b)decrease in symmetry and bond contraction
- c)increase in symmetry and bond contraction
- d)decrease in symmetry and bond elongation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)incr...
Introduction:
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is a molecule with a trigonal planar shape. It consists of a central boron atom bonded to three fluorine atoms. When BF3 reacts with a Lewis base, such as a fluoride ion (F-), it forms a tetrafluoroborate ion (BF4-). This reaction involves the transfer of a fluoride ion from the Lewis base to the boron atom, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond.
Explanation:
The conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate involves changes in both symmetry and bond lengths. Let's explore each of these aspects in detail:
1. Increase in Symmetry:
Symmetry refers to a property of a molecule that describes how its various parts can be interchanged without changing its overall appearance. In the case of BF3, it has a trigonal planar shape and a C3v point group symmetry. On the other hand, the tetrafluoroborate ion (BF4-) has a tetrahedral shape and a Td point group symmetry. Therefore, the conversion of BF3 to BF4- results in an increase in symmetry.
When a molecule undergoes a process that increases its symmetry, it means that its various parts are becoming more equivalent or similar in terms of their positions and interactions. In this case, the conversion of BF3 to BF4- leads to the formation of four equivalent B-F bonds, resulting in increased symmetry.
2. Bond Elongation:
Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. It is influenced by factors such as the size of the atoms and the strength of the bond. When BF3 reacts with F-, the boron atom accepts an additional electron pair, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond between boron and one of the fluorine atoms from the fluoride ion.
The addition of this new bond leads to an increase in the average distance between the boron atom and the fluorine atoms, resulting in bond elongation. The elongation of the B-F bonds in the tetrafluoroborate ion compared to BF3 is a consequence of the new bond formation and the redistribution of electron density in the molecule.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies an increase in symmetry and bond elongation. The formation of the tetrafluoroborate ion results in a molecule with higher symmetry due to the formation of four equivalent B-F bonds. Additionally, the addition of a new covalent bond between boron and fluoride leads to an elongation of the B-F bonds compared to BF3.
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is a molecule with a trigonal planar shape. It consists of a central boron atom bonded to three fluorine atoms. When BF3 reacts with a Lewis base, such as a fluoride ion (F-), it forms a tetrafluoroborate ion (BF4-). This reaction involves the transfer of a fluoride ion from the Lewis base to the boron atom, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond.
Explanation:
The conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate involves changes in both symmetry and bond lengths. Let's explore each of these aspects in detail:
1. Increase in Symmetry:
Symmetry refers to a property of a molecule that describes how its various parts can be interchanged without changing its overall appearance. In the case of BF3, it has a trigonal planar shape and a C3v point group symmetry. On the other hand, the tetrafluoroborate ion (BF4-) has a tetrahedral shape and a Td point group symmetry. Therefore, the conversion of BF3 to BF4- results in an increase in symmetry.
When a molecule undergoes a process that increases its symmetry, it means that its various parts are becoming more equivalent or similar in terms of their positions and interactions. In this case, the conversion of BF3 to BF4- leads to the formation of four equivalent B-F bonds, resulting in increased symmetry.
2. Bond Elongation:
Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. It is influenced by factors such as the size of the atoms and the strength of the bond. When BF3 reacts with F-, the boron atom accepts an additional electron pair, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond between boron and one of the fluorine atoms from the fluoride ion.
The addition of this new bond leads to an increase in the average distance between the boron atom and the fluorine atoms, resulting in bond elongation. The elongation of the B-F bonds in the tetrafluoroborate ion compared to BF3 is a consequence of the new bond formation and the redistribution of electron density in the molecule.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies an increase in symmetry and bond elongation. The formation of the tetrafluoroborate ion results in a molecule with higher symmetry due to the formation of four equivalent B-F bonds. Additionally, the addition of a new covalent bond between boron and fluoride leads to an elongation of the B-F bonds compared to BF3.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)incr...
In BF3 ( Dзh) due to stronger 2p(B)-2p(F) π back bonding; the bond order of each B-F bond is greater than one while in BF4- (Td) bond order of B-F is one therefore conversion of BF3 to BF4- accompanies with bond elongation. Point group Td is a group of high symmetry than Dзh
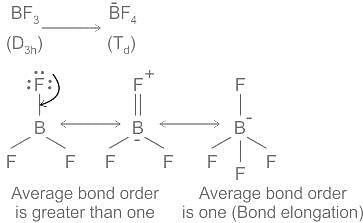
Hence, Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies increase in symmetry and bond elongation.

Hence, Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies increase in symmetry and bond elongation.
Attention UGC NET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed UGC NET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in UGC NET.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2024 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2024 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompaniesa)increase in symmetry and bond elongationb)decrease in symmetry and bond contractionc)increase in symmetry and bond contractiond)decrease in symmetry and bond elongationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























