Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Start Learning for Free
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Verified Answer
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, so they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria.
However, plant cells and animal cells do not look exactly the same or have all of the same organelles, since they each have different needs. For example, plant cells contain chloroplasts since they need to perform photosynthesis, but animal cells do not.
Diagram of a typical animal cell:
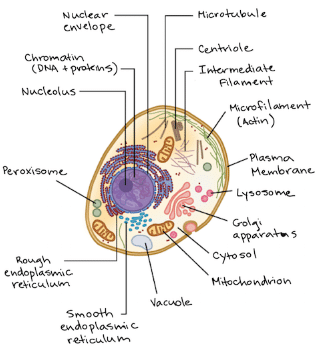
Diagram of a typical plant cell:
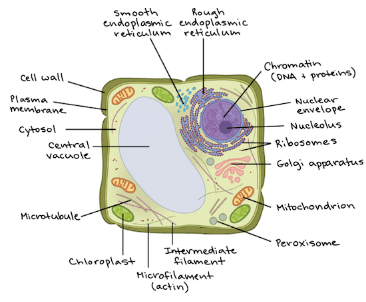

Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don’t get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar from sunlight. This process (photosynthesis) takes place in the chloroplast. Once the sugar is made, it is then broken down by the mitochondria to make energy for the cell. Because animals get sugar from the food they eat, they do not need chloroplasts: just mitochondria.
Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles. A plant cell contains a large, singular vacuole that is used for storage and maintaining the shape of the cell. In contrast, animal cells have many, smaller vacuoles.
Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape. Animal cells simply have a cell membrane, but no cell wall.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Plant Cell
A plant cell is the structural and functional unit of a plant. It is eukaryotic in nature, meaning it has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Here is a detailed description of the components of a plant cell:
Cell Wall: The cell wall is a rigid outer covering that provides structural support and protection to the plant cell. It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.
Cell Membrane: The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the DNA, which carries the genetic information necessary for cell growth, development, and reproduction.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains various organelles and is involved in many cellular processes.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a network of interconnected membranes that are involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes, and smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to their respective destinations within or outside the cell.
Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, which captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
Vacuole: The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products. In plant cells, the vacuole is typically larger than in animal cells and helps maintain cell turgidity.
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes responsible for breaking down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances.
Peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are involved in detoxification processes and the breakdown of fatty acids.
Animal Cell
An animal cell is the basic unit of structure and function in animals. It is also eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Here is a detailed description of the components of an animal cell:
Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the DNA, which carries the genetic information necessary for cell growth, development, and reproduction.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains various organelles and is involved in many cellular processes.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy in the form of adenosine triph
A plant cell is the structural and functional unit of a plant. It is eukaryotic in nature, meaning it has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Here is a detailed description of the components of a plant cell:
Cell Wall: The cell wall is a rigid outer covering that provides structural support and protection to the plant cell. It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.
Cell Membrane: The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the DNA, which carries the genetic information necessary for cell growth, development, and reproduction.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains various organelles and is involved in many cellular processes.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a network of interconnected membranes that are involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes, and smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to their respective destinations within or outside the cell.
Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, which captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
Vacuole: The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products. In plant cells, the vacuole is typically larger than in animal cells and helps maintain cell turgidity.
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes responsible for breaking down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances.
Peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are involved in detoxification processes and the breakdown of fatty acids.
Animal Cell
An animal cell is the basic unit of structure and function in animals. It is also eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Here is a detailed description of the components of an animal cell:
Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the DNA, which carries the genetic information necessary for cell growth, development, and reproduction.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains various organelles and is involved in many cellular processes.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy in the form of adenosine triph
Community Answer
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Give A Short Decription Of Plant And Animal Cell with The Diagram
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?
Question Description
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?.
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?.
Solutions for Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.?, a detailed solution for Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? has been provided alongside types of Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Describe plant and animal cell with diagram.? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























