Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The most common constituents of alkalinity in...
Start Learning for Free
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______
- a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicators
- b)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicators
- c)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicators
- d)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicators
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measur...
Alkalinity is defined as the number of ions in water that will react to hydrogen ion or it is the ability to neutralize acids.
Source:
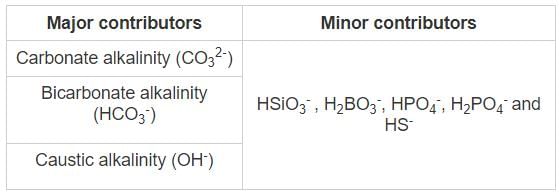
Measurement:
Source:

Measurement:
- By titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using Phenolphthalein and Methyl Orange indicators.
- The relative quantity of alkalinity species is pH-dependent.
- Expressed in terms of mg/l as CaCO3.
Most Upvoted Answer
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measur...
Explanation:
Titration Process:
- The titration process involves adding a measured amount of 0.02 N H2SO4 to the water sample until the endpoint is reached.
Indicators used:
- In this titration, both phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicators are commonly used.
- Phenolphthalein is used to determine the endpoint for the alkalinity caused by hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions.
- Methyl orange is used to detect the endpoint for the total alkalinity in the water sample.
Role of Indicators:
- Phenolphthalein changes color from pink to colorless at a pH of around 8.3-10, indicating the endpoint for hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions.
- Methyl orange changes color from red to yellow at a pH of around 4.4-6.3, indicating the endpoint for total alkalinity.
Choice of Indicators:
- The combination of phenolphthalein and methyl orange ensures accurate determination of the different constituents of alkalinity present in the water sample.
- Using these indicators helps in identifying the endpoint for specific ions present in the water, leading to precise alkalinity measurements.
Therefore, the correct choice for measuring the constituents of alkalinity in natural water by titration with 0.02 N H2SO4 is option 'A' - Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicators.
Titration Process:
- The titration process involves adding a measured amount of 0.02 N H2SO4 to the water sample until the endpoint is reached.
Indicators used:
- In this titration, both phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicators are commonly used.
- Phenolphthalein is used to determine the endpoint for the alkalinity caused by hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions.
- Methyl orange is used to detect the endpoint for the total alkalinity in the water sample.
Role of Indicators:
- Phenolphthalein changes color from pink to colorless at a pH of around 8.3-10, indicating the endpoint for hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions.
- Methyl orange changes color from red to yellow at a pH of around 4.4-6.3, indicating the endpoint for total alkalinity.
Choice of Indicators:
- The combination of phenolphthalein and methyl orange ensures accurate determination of the different constituents of alkalinity present in the water sample.
- Using these indicators helps in identifying the endpoint for specific ions present in the water, leading to precise alkalinity measurements.
Therefore, the correct choice for measuring the constituents of alkalinity in natural water by titration with 0.02 N H2SO4 is option 'A' - Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicators.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The most common constituents of alkalinity in natural water are measured by titrating the water sample with 0.02 N H2SO4 using ______a)Phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicatorsb)Ferrion and phenolphthanlein indicatorsc)Methyl orange and erichrome black T indicatorsd)Erichrome black T and Ferrion indicatorsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























