JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The redox reaction among the following is:a)R...
Start Learning for Free
The redox reaction among the following is:
- a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 with AgNO3
- b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlight
- c)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 K
- d)Reaction of H2SO4 with NaOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3w...
The redox reaction is:
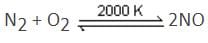
Nitrogen is oxidised, while oxygen is reduced. Reaction of [CO(H2O)6]Cl3 with AgNO3 is not a redox reaction. It is a precipitation reaction.

Nitrogen is oxidised, while oxygen is reduced. Reaction of [CO(H2O)6]Cl3 with AgNO3 is not a redox reaction. It is a precipitation reaction.
Most Upvoted Answer
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3w...
The redox reaction among the given options is the combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 K (option C).
Combination of Dinitrogen with Dioxygen:
- This reaction involves the combination of dinitrogen (N2) with dioxygen (O2) to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
- The reaction can be represented as follows: N2 + O2 → 2NO2
- In this reaction, the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from 0 to +4, and the oxidation state of oxygen changes from 0 to -2.
- This indicates that nitrogen is being oxidized, while oxygen is being reduced.
- The oxidation state of an element refers to the distribution of its electrons in a compound or ion.
- When nitrogen combines with oxygen, the oxidation state of nitrogen increases from 0 to +4, indicating that it has lost electrons and, therefore, has been oxidized.
- On the other hand, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases from 0 to -2, indicating that it has gained electrons and, therefore, has been reduced.
- Since this reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, it is a redox reaction.
Explanation:
- Option A, the reaction between [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 and AgNO3, does not involve any change in oxidation states. It is a precipitation reaction, not a redox reaction.
- Option B, the formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlight, is not a redox reaction. It is a photochemical reaction that involves the conversion of oxygen molecules into ozone molecules.
- Option D, the reaction of H2SO4 with NaOH, is a neutralization reaction where sulfuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form water and sodium sulfate. It does not involve any change in oxidation states.
- Thus, the correct answer is option C, the combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 K. This reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, making it a redox reaction.
Combination of Dinitrogen with Dioxygen:
- This reaction involves the combination of dinitrogen (N2) with dioxygen (O2) to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
- The reaction can be represented as follows: N2 + O2 → 2NO2
- In this reaction, the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from 0 to +4, and the oxidation state of oxygen changes from 0 to -2.
- This indicates that nitrogen is being oxidized, while oxygen is being reduced.
- The oxidation state of an element refers to the distribution of its electrons in a compound or ion.
- When nitrogen combines with oxygen, the oxidation state of nitrogen increases from 0 to +4, indicating that it has lost electrons and, therefore, has been oxidized.
- On the other hand, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases from 0 to -2, indicating that it has gained electrons and, therefore, has been reduced.
- Since this reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, it is a redox reaction.
Explanation:
- Option A, the reaction between [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 and AgNO3, does not involve any change in oxidation states. It is a precipitation reaction, not a redox reaction.
- Option B, the formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlight, is not a redox reaction. It is a photochemical reaction that involves the conversion of oxygen molecules into ozone molecules.
- Option D, the reaction of H2SO4 with NaOH, is a neutralization reaction where sulfuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form water and sodium sulfate. It does not involve any change in oxidation states.
- Thus, the correct answer is option C, the combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 K. This reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, making it a redox reaction.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The redox reaction among the following is:a)Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]Cl3with AgNO3b)Formation of ozone from atmospheric oxygen in the presence of sunlightc)Combination of dinitrogen with dioxygen at 2000 Kd)Reaction of H2SO4with NaOHCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























