Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > This section contains 12 multiple choice ques...
Start Learning for Free
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B is
- a)0.50
- b)0.25
- c)0.45
- d)0.75
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has ...
In solution containing several non-volatile solutes, the lowering of the vapour pressure depends on the sum of the mole fraction of different solutes.This translates to the equation p^0−p/p^0 = x2, the expression on the left hand side is called the relative lowering of vapour pressure and is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.0.80−0.60/0.80 = x2 = 0.25
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has ...
Question:
The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B is
Answer:
To find the mole fraction of component B, we need to understand the relationship between the vapor pressure and mole fraction of a solute in a solution.
Vapor Pressure:
The vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its vapor when it is in equilibrium with its liquid phase. In a solution, the vapor pressure of the solvent decreases due to the presence of a non-volatile solute. This decrease in vapor pressure is proportional to the mole fraction of the solute in the solution.
Mole Fraction:
The mole fraction of a component in a solution is the ratio of the number of moles of that component to the total number of moles in the solution.
Given:
Vapor pressure of pure liquid solvent (Ps) = 0.80 atm
Vapor pressure of solution (P) = 0.60 atm
Using the Raoult's Law equation:
P = Ps * Xs
Where P is the vapor pressure of the solution, Ps is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent, and Xs is the mole fraction of the solvent.
Solving for Xs:
0.60 atm = 0.80 atm * Xs
Dividing both sides by 0.80 atm:
Xs = 0.60 atm / 0.80 atm
Simplifying:
Xs = 0.75
Thus, the mole fraction of the component B (solute) is 0.75.
Answer:
The correct answer is (d) 0.75.
The vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B is
Answer:
To find the mole fraction of component B, we need to understand the relationship between the vapor pressure and mole fraction of a solute in a solution.
Vapor Pressure:
The vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its vapor when it is in equilibrium with its liquid phase. In a solution, the vapor pressure of the solvent decreases due to the presence of a non-volatile solute. This decrease in vapor pressure is proportional to the mole fraction of the solute in the solution.
Mole Fraction:
The mole fraction of a component in a solution is the ratio of the number of moles of that component to the total number of moles in the solution.
Given:
Vapor pressure of pure liquid solvent (Ps) = 0.80 atm
Vapor pressure of solution (P) = 0.60 atm
Using the Raoult's Law equation:
P = Ps * Xs
Where P is the vapor pressure of the solution, Ps is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent, and Xs is the mole fraction of the solvent.
Solving for Xs:
0.60 atm = 0.80 atm * Xs
Dividing both sides by 0.80 atm:
Xs = 0.60 atm / 0.80 atm
Simplifying:
Xs = 0.75
Thus, the mole fraction of the component B (solute) is 0.75.
Answer:
The correct answer is (d) 0.75.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has ...
Using Raoults law for lowering of vapour pressure.We get 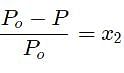
putting,Values of actual and lowered vapour pressure we get
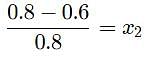
where x2 is the mole fraction .
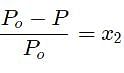
putting,Values of actual and lowered vapour pressure we get
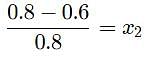
where x2 is the mole fraction .

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent is 0.80 atm. When a non-volatile solute B is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure drops to 0.60 atm. Thus, mole fraction of the component B isa)0.50b)0.25c)0.45d)0.75Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















