Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombin...
Start Learning for Free
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes
A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal.
B.
E.
coli
with mutated dna b gene does not survive.
C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands
D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair
The correct combinations are:
- a)A and B
- b)B and C
- c)A and C
- d)A and D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair a...
Concept:
- Recombination repair is a mechanism for generating a functional DNA molecule from two damaged molecules.
- It is an essential repair process for dividing cells because a replication fork may arrive at a damaged site, such as a thymine dimer, before the excision repair system has eliminated damage.
- The dnaB protein is a DNA helicase that is capable of unwinding extensive stretches of double-stranded DNA.
Explanation:
Fig 1:
The four cellular functions of the RecA protein in Escherichia coli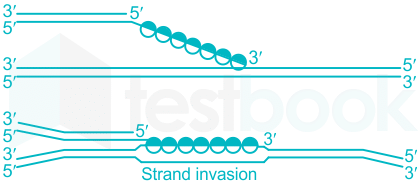
(A) RecA protein is involved in many aspects of recombinational DNA repair, and promotes a variety of DNA strand exchange reactions in the context of this function.
- One key type of reaction is shown-DNA strand invasion.
- In this process, RecA forms a filament (RecA*) on the 3′ end of a single-stranded DNA, aligns that DNA with its complement in a duplex DNA, and pairs the bound DNA with the complementary strand of the duplex (displacing the other duplex strand).
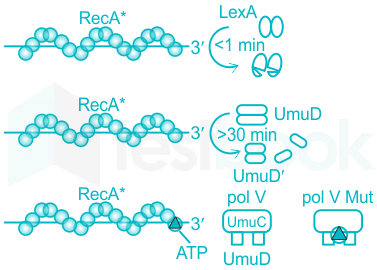
(B) The autocatalytic cleavage of LexA repressor occurs rapidly in the presence of RecA* filaments.
- It is the number and extent of filament formation that governs the efficiency of LexA auto cleavage.
- As a result of excessive DNA damage, the number of single strand DNA gaps is increased.
- LexA cleavage and the accompanying SOS system induction generally occur only in response to such damage.
(C) RecA* is required for the autocatalytic cleavage of the UmuD protein to form active UmuD′.
- This reaction is much slower than LexA cleavage and occurs >30 min after DNA damage.
(D) A RecA monomer and a molecule of ATP are transferred to pol V from the 3′-proximal end of a RecA* filament to form the active pol V Mut.
Fig 2: dna b function in replisome
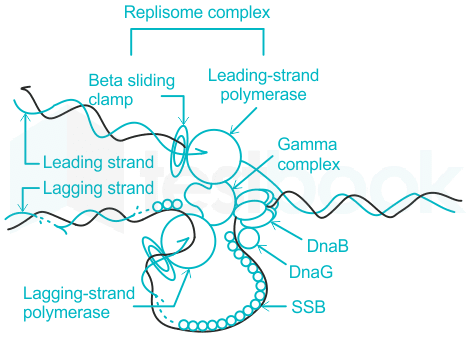
- The dnaB helicase depends on the presence of a hydrolyzable ribonucleoside triphosphate, is maximally stimulated by a combination of E. coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein and E. coli primase, is inhibited by antibody directed against dnaB protein, and is inhibited by prior coating of the single-stranded regions of the helicase substrate with the E. coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein.
- It was determined that the dnaB protein moves 5' to 3' along single-stranded DNA, apparently in a processive fashion.
- To invade the duplex portion of the helicase substrate, the dnaB protein requires a 3'-terminal extension of single-stranded DNA in the strand to which it is not bound.
Statement A:
mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal.
- Consider the explanation above thus this option is not true
Statement B:
E.
coli
with mutated dna b gene does not survive
- Consider the explanation above thus this option is true
Statement C:
dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands
- Consider the explanation above thus this option is true
Statement A:
rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair
- Consider the explanation above thus this option is not true
hence the correct answer is option 2
Most Upvoted Answer
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair a...
Explanation:
Rec A gene:
- The mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal as it is involved in recombination and repair processes.
- Rec A gene plays a crucial role in repairing DNA damage, promoting genetic diversity through recombination, and facilitating the SOS response.
Dna B gene:
- E. coli with a mutated dna B gene can survive, but it may have impaired DNA replication due to the gene's role in unwinding DNA double strands during replication.
- Dna B helps in preventing the annealing of separated DNA strands, allowing for the proper unwinding and replication of DNA.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
B. E. coli with mutated dna B gene does not survive.
Rec A gene:
- The mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal as it is involved in recombination and repair processes.
- Rec A gene plays a crucial role in repairing DNA damage, promoting genetic diversity through recombination, and facilitating the SOS response.
Dna B gene:
- E. coli with a mutated dna B gene can survive, but it may have impaired DNA replication due to the gene's role in unwinding DNA double strands during replication.
- Dna B helps in preventing the annealing of separated DNA strands, allowing for the proper unwinding and replication of DNA.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
B. E. coli with mutated dna B gene does not survive.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Question Description
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In E. coli rec A gene is involved in recombination as well as repair and dna b gene is involved in unwinding of DNA double strands during replication which of the following statements is correct about rec A and dna b genes A. mutation in E. coli rec A gene is lethal. B. E. coli with mutated dna b gene does not survive. C. dna B after uncoiling DNA double stands prevents further the annealing of the separated strands D. rec A gene is involved in SOS response and helps DNA repair The correct combinations are: a)A and Bb)B and Cc)A and Cd)A and DCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















