Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > Ecological compression differs from character...
Start Learning for Free
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on a
- a)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.
- b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.
- c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.
- d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it ...
Concept:
- The study of adaptation—a central issue in biology since before the time of Darwin—is currently enjoying a renaissance.
- The theory of ecological character displacement was first explicitly developed by W. L. Brown and E. O. Wilson in 1956 .
- The idea underlying this theory is quite simple: Suppose that two very similar species come into contact.
- If resources are limiting, the species are likely to compete strongly.
- One possible outcome is competitive exclusion: the superior competitor will triumph and the inferior one will become extinct.
- But an alternative possibility is that natural selection will favor, in each population, those individuals whose phenotype allows them to use resources not used by members of the other species.
Explanation:
Fig 1: Character displacement
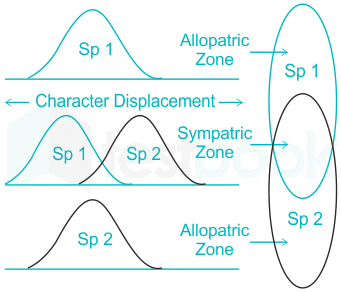
- Character displacement is the term used to describe an evolutionary change that occurs when two similar species inhabit the same environment.
- Under such conditions, natural selection favors a divergence in the characters--morphology, ecology, behavior, or physiology--of the organisms.
- The best example of Character displacement is in the Galapagos Islands, a group of coexisting finches have distinctly different body and beak sizes as well as beak shapes.
- Moreover, character displacement in traits associated with resource use (ecological character displacement) has been studied largely independently of that in traits associated with reproduction (reproductive character displacement).
- The Ecological compression hypothesis predicts that when two species occur together in narrow sympatry, individuals in the overlap zone will use a smaller range of habitats or compress to reduce competition between species and a larger or unchanged range of prey than individuals in allopatry.
- This phenomena shows results in shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.
Fig 2: Niche Compression
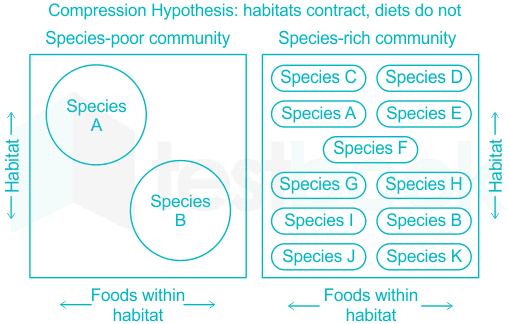

hence the correct answer is option
1Most Upvoted Answer
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it ...
Understanding Ecological Compression and Character Displacement
Ecological compression and character displacement are both concepts in ecology that explain how species interact and adapt to their environments. However, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and timescales.
Ecological Compression
- Definition: Ecological compression refers to a process where species experience a reduction in their ecological niche due to competition for resources, often leading to overlapping resource use.
- Timescale: This phenomenon occurs over a shorter timescale as species respond rapidly to changes in their environment or competition.
- Heritable Change: It does not inherently involve genetic changes or adaptations passed down through generations. Instead, it reflects immediate behavioral or ecological adjustments.
Character Displacement
- Definition: Character displacement involves evolutionary changes that occur when two species interact closely, leading to differences in traits that reduce competition.
- Timescale: This process operates over a longer timescale, as it requires significant evolutionary changes to occur, often spanning many generations.
- Heritable Change: Character displacement typically involves heritable traits that evolve in response to selective pressures from interspecific competition.
Key Differences
- Shorter vs. Longer Timescale: Ecological compression happens quickly, while character displacement evolves over a longer period.
- Heritable vs. Non-Heritable Change: Ecological compression does not involve heritable changes, whereas character displacement is rooted in genetic modifications.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'A' because ecological compression operates on shorter timescales and does not involve heritable changes, distinguishing it clearly from character displacement.
Ecological compression and character displacement are both concepts in ecology that explain how species interact and adapt to their environments. However, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and timescales.
Ecological Compression
- Definition: Ecological compression refers to a process where species experience a reduction in their ecological niche due to competition for resources, often leading to overlapping resource use.
- Timescale: This phenomenon occurs over a shorter timescale as species respond rapidly to changes in their environment or competition.
- Heritable Change: It does not inherently involve genetic changes or adaptations passed down through generations. Instead, it reflects immediate behavioral or ecological adjustments.
Character Displacement
- Definition: Character displacement involves evolutionary changes that occur when two species interact closely, leading to differences in traits that reduce competition.
- Timescale: This process operates over a longer timescale, as it requires significant evolutionary changes to occur, often spanning many generations.
- Heritable Change: Character displacement typically involves heritable traits that evolve in response to selective pressures from interspecific competition.
Key Differences
- Shorter vs. Longer Timescale: Ecological compression happens quickly, while character displacement evolves over a longer period.
- Heritable vs. Non-Heritable Change: Ecological compression does not involve heritable changes, whereas character displacement is rooted in genetic modifications.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'A' because ecological compression operates on shorter timescales and does not involve heritable changes, distinguishing it clearly from character displacement.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Question Description
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ecological compression differs from character displacement in that it operates on aa)shorter timescale and does not involve heritable change.b)longer timescale and does not involve heritable change.c)shorter timescale and involves heritable change.d)longer timescale and involves heritable change.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















