Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygo...
Start Learning for Free
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?
- a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in school
- b)Modelling is a principal way for children to learn
- c)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.
- d)Cognitive development is independent of social development
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the fo...
Lev Vygotsky', a Soviet psychologist, has propounded the "Socio-cultural Theory". This theory implies the idea that social interaction plays a crucial role in the development of learner's cognitive ability.
- According to Vygotsky, social interaction is the primary cause of cognitive development.
- He emphasizes that socialization is essential for learning and should be given priority in school.
- Social development influences cognitive development.
- His theory emphasizes that children learn through interaction and collaboration with skilled and knowledgeable people.
Lev Vygotsky emphasizes the importance of social interaction in his theory by introducing three concepts which are as follows:
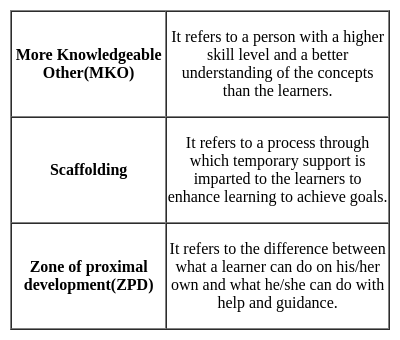
Hence, we can conclude that According to the sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, socialization is essential for learning and should be given priority in school.
Additional Information
- According to the theory of social learning Albert Bandura, modeling is a principal way for children to learn.
- According to Erikson: He developed the theory of psychosocial development which states that the personality of a child evolves through various stages. And an unresolved crisis can harm a child as it will affect the development of his personality which will not come as expected.
Most Upvoted Answer
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the fo...
Understanding Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory emphasizes the fundamental role of social interaction in cognitive development. His perspective is that learning is inherently a social process, deeply rooted in the cultural context.
Socialization as a Learning Priority
- Essential for Learning: Vygotsky believed that socialization is crucial for cognitive growth. Through interactions with others, children internalize knowledge and develop higher-order thinking skills.
- Collaborative Learning: Learning is seen as a collaborative process where children engage with peers and adults, gaining insights and skills that they may not acquire in isolation.
Modelling and Cognitive Development
- While modelling (option b) is significant in learning, it is part of the broader context of social interactions that Vygotsky highlights. Therefore, while true, it does not capture the essence of his primary focus on socialization.
Impact of Unresolved Crises
- Option c refers to Erikson’s theory rather than Vygotsky’s. Thus, it is not applicable when discussing Vygotsky’s views.
Independence of Cognitive Development
- Option d contradicts Vygotsky’s central tenet. He posited that cognitive development cannot be separated from social development; they are interdependent.
Conclusion
In summary, Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory asserts that socialization plays a vital role in learning processes. By prioritizing social interaction in educational settings, we align with Vygotsky’s belief that cognitive development is fundamentally intertwined with cultural and social experiences. This understanding informs effective teaching practices and fosters a collaborative learning environment.
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory emphasizes the fundamental role of social interaction in cognitive development. His perspective is that learning is inherently a social process, deeply rooted in the cultural context.
Socialization as a Learning Priority
- Essential for Learning: Vygotsky believed that socialization is crucial for cognitive growth. Through interactions with others, children internalize knowledge and develop higher-order thinking skills.
- Collaborative Learning: Learning is seen as a collaborative process where children engage with peers and adults, gaining insights and skills that they may not acquire in isolation.
Modelling and Cognitive Development
- While modelling (option b) is significant in learning, it is part of the broader context of social interactions that Vygotsky highlights. Therefore, while true, it does not capture the essence of his primary focus on socialization.
Impact of Unresolved Crises
- Option c refers to Erikson’s theory rather than Vygotsky’s. Thus, it is not applicable when discussing Vygotsky’s views.
Independence of Cognitive Development
- Option d contradicts Vygotsky’s central tenet. He posited that cognitive development cannot be separated from social development; they are interdependent.
Conclusion
In summary, Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory asserts that socialization plays a vital role in learning processes. By prioritizing social interaction in educational settings, we align with Vygotsky’s belief that cognitive development is fundamentally intertwined with cultural and social experiences. This understanding informs effective teaching practices and fosters a collaborative learning environment.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice According to the Sociocultural theory of Vygotsky, which one of the following is true?a)Socialisation is essential for learning and should be given priority in schoolb)Modelling is a principal way for children to learnc)An unresolved crisis can harm a child.d)Cognitive development is independent of social developmentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























