Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Di...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?
- a)Successive Approximation Converter
- b)Counter Type
- c)Dual Slope Converter
- d)R-2R Ladder
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Success...
Concept:
The common Analog to digital converters are:
Ramp-type:
- The principle of Ramp-type DVM is based on the measurement of the time it takes for a linear ramp voltage to rise from 0 V to the level of the input voltage (or) to decrease from the level of the input voltage to zero.
- This type of Analogue to Digital Converter is very slow (but cheap and simple).
- It is ideal for data that changes fairly slowly such as vehicle or aircraft control systems.
- Audio signals are slow enough to be converted.
Dual-slope converter:
- In the dual-slope technique, an integrator is used to integrate an accurate voltage reference for a fixed period of time. The same integrator is then used to integrate with the reverse slope, the input voltage, and the time required to return to the starting voltage is measured.
- The automatic zero correction function is performed before each conversion so that changes in the offset voltages & current will be compensated.
Successive Approximation:
- The basic principle is binary regression, in which analog input is compared with DAC reference voltage which is repeatedly divided in half.
- A successive approximation A/D converter consists of a comparator, a successive approximation register (SAR), output latches, and a D/A converter.
- It is capable of high speed and is reliable.
Important Points
R-2R ladder is used for Digital to Analog Converter:
It uses a summing amplifier with an R-2R ladder network as shown below.
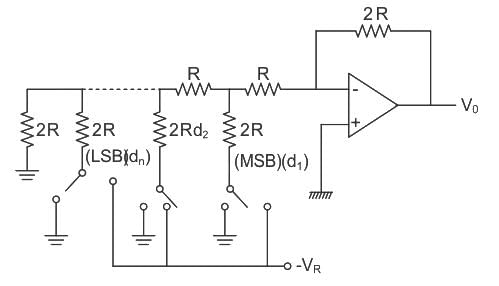
For n-bit DAC, it requires only 2 different values of resistors i.e. R and 2R.
It uses a summing amplifier with an R-2R ladder network as shown below.

For n-bit DAC, it requires only 2 different values of resistors i.e. R and 2R.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Success...
Understanding Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are essential components in electronic systems that convert continuous analog signals into discrete digital values. While there are several types of ADCs, one option mentioned in the question is not an ADC.
Types of ADCs
- Successive Approximation Converter:
This type uses a binary search algorithm to converge on the value of the input voltage, making it efficient and widely used in applications requiring moderate speed and accuracy.
- Counter Type (or Ramp Converter):
This ADC counts up or down until it matches the input voltage. It is simple and can be accurate, though it typically has slower conversion times compared to other types.
- Dual Slope Converter:
This converter integrates the input signal over a period and then measures the time required to discharge it. It is known for its high accuracy and is commonly used in digital voltmeters.
R-2R Ladder: The Non-ADC
- R-2R Ladder:
This is actually a type of digital-to-analog converter (DAC), not an ADC. It utilizes a network of resistors in a ladder configuration to create analog voltages from binary inputs. Its primary function is to convert digital signals back into analog form, which is the opposite of what ADCs do.
Conclusion
In summary, while options A, B, and C are all types of ADCs, option D, the R-2R Ladder, is a DAC. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for those working in electrical engineering and related fields.
Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are essential components in electronic systems that convert continuous analog signals into discrete digital values. While there are several types of ADCs, one option mentioned in the question is not an ADC.
Types of ADCs
- Successive Approximation Converter:
This type uses a binary search algorithm to converge on the value of the input voltage, making it efficient and widely used in applications requiring moderate speed and accuracy.
- Counter Type (or Ramp Converter):
This ADC counts up or down until it matches the input voltage. It is simple and can be accurate, though it typically has slower conversion times compared to other types.
- Dual Slope Converter:
This converter integrates the input signal over a period and then measures the time required to discharge it. It is known for its high accuracy and is commonly used in digital voltmeters.
R-2R Ladder: The Non-ADC
- R-2R Ladder:
This is actually a type of digital-to-analog converter (DAC), not an ADC. It utilizes a network of resistors in a ladder configuration to create analog voltages from binary inputs. Its primary function is to convert digital signals back into analog form, which is the opposite of what ADCs do.
Conclusion
In summary, while options A, B, and C are all types of ADCs, option D, the R-2R Ladder, is a DAC. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for those working in electrical engineering and related fields.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is NOT an Analog-to-Digital Converter?a)Successive Approximation Converterb)Counter Typec)Dual Slope Converterd)R-2R LadderCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















